Activity-dependent release of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor from primary sensory neurons detected by ELISA in situ
- PMID: 11007900
- PMCID: PMC6772775
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07417.2000
Activity-dependent release of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor from primary sensory neurons detected by ELISA in situ
Abstract
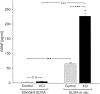
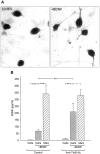
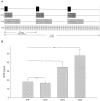
To define activity-dependent release of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), we developed an in vitro model using primary sensory neurons and a modified ELISA, termed ELISA in situ. Dissociate cultures of nodose-petrosal ganglion cells from newborn rats were grown in wells precoated with anti-BDNF antibody to capture released BDNF, which was subsequently detected using conventional ELISA. Conventional ELISA alone was unable to detect any increase in BDNF concentration above control values following chronic depolarization with 40 mM KCl for 72 hr. However, ELISA in situ demonstrated a highly significant increase in BDNF release, from 65 pg/ml in control to 228 pg/ml in KCl-treated cultures. The efficacy of the in situ assay appears to be related primarily to rapid capture of released BDNF that prevents BDNF binding to the cultured cells. We therefore used this approach to compare BDNF release from cultures exposed for 30 min to either continuous depolarization with elevated KCl or patterned electrical field stimulation (50 biphasic rectangular pulses of 25 msec, at 20 Hz, every 5 sec). Short-term KCl depolarization was completely ineffective at evoking any detectable release of BDNF, whereas patterned electrical stimulation increased extracellular BDNF levels by 20-fold. In addition, the magnitude of BDNF release was dependent on stimulus pattern, with high-frequency bursts being most effective. These data indicate that the optimal stimulus profile for BDNF release resembles that of other neuroactive peptides. Moreover, our findings demonstrate that BDNF release can encode temporal features of presynaptic neuronal activity.
Figures


References
-
- Acheson A, Lindsay RM. Non target-derived roles of the neurotrophins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996;351:417–422. - PubMed
-
- Agoston DV, Conlon JM, Whittaker VP. Selective depletion of the acetylcholine and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide of the guinea-pig myenteric plexus by differential mobilization of distinct transmitter pools. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72:535–542. - PubMed
-
- Androutsellis-Theotokis A, McCormack WJ, Bradford HF, Stern GM, Pliego-Rivero FB. The depolarisation-induced release of [125I]BDNF from brain tissue. Brain Res. 1996;743:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Apfel SC, Wright DE, Wiideman AM, Dormia C, Snider WD, Kessler JA. Nerve growth factor regulates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the peripheral nervous system. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7:134–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
