Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice
- PMID: 11009421
- PMCID: PMC3582399
- DOI: 10.1126/science.289.5488.2350
Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice
Abstract
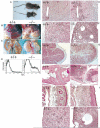
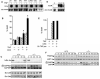
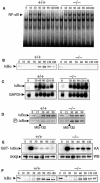
A20 is a cytoplasmic zinc finger protein that inhibits nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated programmed cell death (PCD). TNF dramatically increases A20 messenger RNA expression in all tissues. Mice deficient for A20 develop severe inflammation and cachexia, are hypersensitive to both lipopolysaccharide and TNF, and die prematurely. A20-deficient cells fail to terminate TNF-induced NF-kappaB responses. These cells are also more susceptible than control cells to undergo TNF-mediated PCD. Thus, A20 is critical for limiting inflammation by terminating TNF-induced NF-kappaB responses in vivo.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

