Pacific Northwest marine sediments contain ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the beta subdivision of the Proteobacteria
- PMID: 11010911
- PMCID: PMC92337
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.10.4532-4535.2000
Pacific Northwest marine sediments contain ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in the beta subdivision of the Proteobacteria
Abstract
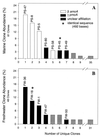
The diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in aquatic sediments was studied by retrieving ammonia monooxygenase and methane monooxygenase gene sequences. Methanotrophs dominated freshwater sediments, while beta-proteobacterial ammonia oxidizers dominated marine sediments. These results suggest that gamma-proteobacteria such as Nitrosococcus oceani are minor members of marine sediment ammonia-oxidizing communities.
Figures

References
-
- Hartnett H E. Organic carbon input, degradation and preservation in continental margin sediments: an assessment of the role of a strong oxygen deficient zone. Ph.D. thesis. Seattle: University of Washington; 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

