Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group
- PMID: 11010916
- PMCID: PMC92342
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.10.4555-4558.2000
Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group
Abstract
Phylogenetic analysis has shown that Escherichia coli is composed of four main phylogenetic groups (A, B1, B2, and D) and that virulent extra-intestinal strains mainly belong to groups B2 and D. Actually, phylogenetic groups can be determined by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis or ribotyping, both of which are complex, time-consuming techniques. We describe a simple and rapid phylogenetic grouping technique based on triplex PCR. The method, which uses a combination of two genes (chuA and yjaA) and an anonymous DNA fragment, was tested with 230 strains and showed excellent correlation with reference methods.
Figures
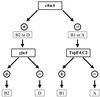

References
-
- Belgrader P, Benett W, Hadley D, Long G, Mariella R, Jr, Milanovich F, Nasarabadi S, Nelson W, Richards J, Stratton P. Rapid pathogen detection using a microchip PCR array instrument. Clin Chem. 1998;44:2191–2194. - PubMed
-
- Bingen E, Denamur E, Brahimi N, Elion J. Genotyping may provide rapid identification of Escherichia coli K1 organisms that cause neonatal meningitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:152–156. - PubMed
-
- Bingen E, Picard B, Brahimi N, Mathy S, Desjardins P, Elion J, Denamur E. Phylogenetic analysis of Escherichia coli strains causing neonatal meningitis suggests horizontal gene transfer from a predominant pool of highly virulent B2 group strains. J Infect Dis. 1998;177:642–650. - PubMed
-
- Blattner F R, Plunkett G I, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D, Rode C K, Mayew G F, Gregor J, Davis N W, Kirkpatrick H A, Goeden M A, Rose D J, Mau B, Shao Y. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

