Targeting the chromatin-remodeling MSL complex of Drosophila to its sites of action on the X chromosome requires both acetyl transferase and ATPase activities
- PMID: 11013222
- PMCID: PMC302094
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.19.5202
Targeting the chromatin-remodeling MSL complex of Drosophila to its sites of action on the X chromosome requires both acetyl transferase and ATPase activities
Abstract
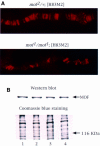
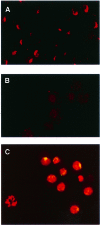
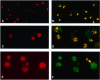
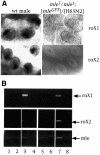
Dosage compensation in Drosophila is mediated by a multiprotein, RNA-containing complex that associates with the X chromosome at multiple sites. We have investigated the role that the enzymatic activities of two complex components, the histone acetyltransferase activity of MOF and the ATPase activity of MLE, may have in the targeting and association of the complex with the X chromosome. Here we report that MLE and MOF activities are necessary for complexes to access the various X chromosome sites. The role that histone H4 acetylation plays in this process is supported by our observations that MOF overexpression leads to the ectopic association of the complex with autosomal sites.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The roX genes encode redundant male-specific lethal transcripts required for targeting of the MSL complex.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1084. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11867536 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of MOF, a putative histone acetyl transferase, to the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Genet. 1998;22(1):56-64. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1998)22:1<56::AID-DVG6>3.0.CO;2-6. Dev Genet. 1998. PMID: 9499580
-
Sex-biased transcription enhancement by a 5' tethered Gal4-MOF histone acetyltransferase fusion protein in Drosophila.BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Nov 9;11:80. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-80. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 21062452 Free PMC article.
-
The right dose for every sex.Chromosoma. 2007 Apr;116(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0089-x. Epub 2006 Nov 24. Chromosoma. 2007. PMID: 17124606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin mechanisms in Drosophila dosage compensation.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2005;38:123-49. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27310-7_5. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15881893 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc finger protein Zn72D promotes productive splicing of the maleless transcript.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(24):8760-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01415-07. Epub 2007 Oct 8. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17923683 Free PMC article.
-
The MLE subunit of the Drosophila MSL complex uses its ATPase activity for dosage compensation and its helicase activity for targeting.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Feb;28(3):958-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00995-07. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18039854 Free PMC article.
-
The roX genes encode redundant male-specific lethal transcripts required for targeting of the MSL complex.EMBO J. 2002 Mar 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.5.1084. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11867536 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila roX1 RNA gene can overcome silent chromatin by recruiting the male-specific lethal dosage compensation complex.Genetics. 2003 Jun;164(2):565-74. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.2.565. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12807777 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation in Drosophila.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 May 1;7(5):a019398. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019398. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25934013 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhtar A. and Becker,P.B. (2000) Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell, 5, 367–375. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A., Zinc,D. and Becker,P.B. (2000) Chromodomains are protein–RNA interaction modules. Nature, in press. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw G.J. and Baker,B.S. (1995) The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex-specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development, 121, 3245–3258. - PubMed
-
- Bone J.R., Lavender,J., Richman,R., Palmer,M.J., Turner,B.M. and Kuroda,M.I. (1994) Acetylated histone H4 on the male X chromosome is associated with dosage compensation in Drosophila. Genes Dev., 8, 96–104. - PubMed
-
- Borrow J. et al. (1996) The translocation t(8;16)(p11;p13) of acute myeloid leukaemia fuses a putative acetyltransferase to the CREB-binding protein. Nature Genet., 14, 33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

