Use of amplified fragment length polymorphisms for typing Corynebacterium diphtheriae
- PMID: 11015416
- PMCID: PMC87489
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.10.3843-3845.2000
Use of amplified fragment length polymorphisms for typing Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Abstract
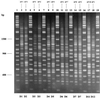
Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was investigated for the differentiation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae isolates. Analysis using Taxotron revealed 10 distinct AFLP profiles among 57 isolates. Strains with ribotype patterns D1, D4, and D12 could not be distinguished; however, the technique discriminated isolates of ribotype patterns D3, D6, and D7 further. AFLP was rapid, fairly inexpensive, and reproducible and could be used as an alternative to ribotyping.
Figures

References
-
- Boumedine K S, Rodolakis A. AFLP allows the identification of genomic markers of ruminant Chlamydia psittaci strains useful for typing and epidemiological studies. Res Microbiol. 1998;149:735–744. - PubMed
-
- De Zoysa A S, Efstratiou A. PCR typing of Corynebacterium diphtheriae by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. J Med Microbiol. 1999;48:335–340. - PubMed
-
- De Zoysa A, Efstratiou A, George R C, Jahkola M, Vuopio-Varkila J, Deshevoi S, Tseneva G, Rikushin Y. Molecular epidemiology of Corynebacterium diphtheriae from northwestern Russia and surrounding countries studied by using ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:1080–1083. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dittmann S, Wharton M, Vitek C, Ciotti M, Galazka A, Guichard S, Hardy I, Kartoglu U, Koyama S, Kreysler J, Martin B, Mercer D, Ronne T, Roure C, Steinglass R, Strebel P. Successful control of epidemic diphtheria in the states of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics: lessons learned. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:S10–S22. - PubMed
-
- Galazka A. The immunological basis for immunisation: diphtheria. Module 2, Expanded Programme on Immunisation. WHO/EP/GEN/93.12. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

