Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation
- PMID: 11015443
- PMCID: PMC2193311
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.7.1027
Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation
Abstract
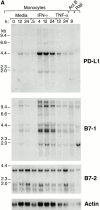
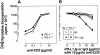
PD-1 is an immunoinhibitory receptor expressed by activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells. Mice deficient in PD-1 exhibit a breakdown of peripheral tolerance and demonstrate multiple autoimmune features. We report here that the ligand of PD-1 (PD-L1) is a member of the B7 gene family. Engagement of PD-1 by PD-L1 leads to the inhibition of T cell receptor-mediated lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine secretion. In addition, PD-1 signaling can inhibit at least suboptimal levels of CD28-mediated costimulation. PD-L1 is expressed by antigen-presenting cells, including human peripheral blood monocytes stimulated with interferon gamma, and activated human and murine dendritic cells. In addition, PD-L1 is expressed in nonlymphoid tissues such as heart and lung. The relative levels of inhibitory PD-L1 and costimulatory B7-1/B7-2 signals on antigen-presenting cells may determine the extent of T cell activation and consequently the threshold between tolerance and autoimmunity. PD-L1 expression on nonlymphoid tissues and its potential interaction with PD-1 may subsequently determine the extent of immune responses at sites of inflammation.
Figures








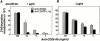
References
-
- Agata Y., Kawasaki A., Nishimura H., Ishida Y., Tsubata T., Yagita H., Honjo T. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 1996;8:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Vibhakar R., Juan G., Traganos F., Darzynkiewicz Z., Finger L.R. Activation-induced expression of human programmed death-1 gene in T-lymphocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 1997;232:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Shinohara T., Taniwaki M., Ishida Y., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human PD-1 gene (PDCD1) Genomics. 1994;23:704–706. - PubMed
-
- Vivier E., Daeron M. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs. Immunol. Today. 1997;18:286–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

