High-affinity ouabain binding by a chimeric gastric H+,K+-ATPase containing transmembrane hairpins M3-M4 and M5-M6 of the alpha 1-subunit of rat Na+,K+-ATPase
- PMID: 11016952
- PMCID: PMC17179
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.200109597
High-affinity ouabain binding by a chimeric gastric H+,K+-ATPase containing transmembrane hairpins M3-M4 and M5-M6 of the alpha 1-subunit of rat Na+,K+-ATPase
Abstract
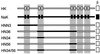
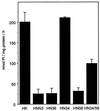
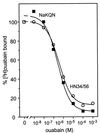
Na(+),K(+)-ATPase and gastric H(+),K(+)-ATPase are two related enzymes that are responsible for active cation transport. Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity is inhibited specifically by ouabain, whereas H(+),K(+)-ATPase is insensitive to this drug. Because it is not known which parts of the catalytic subunit of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase are responsible for ouabain binding, we prepared chimeras in which small parts of the alpha-subunit of H(+),K(+)-ATPase were replaced by their counterparts of the alpha(1)-subunit of rat Na(+),K(+)-ATPase. A chimeric enzyme in which transmembrane segments 5 and 6 of H(+), K(+)-ATPase were replaced by those of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase could form a phosphorylated intermediate, but hardly showed a K(+)-stimulated dephosphorylation reaction. When transmembrane segments 3 and 4 of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase were also included in this chimeric ATPase, K(+)-stimulated dephosphorylation became apparent. This suggests that there is a direct interaction between the hairpins M3-M4 and M5-M6. Remarkably, this chimeric enzyme, HN34/56, had obtained a high-affinity ouabain-binding site, whereas the rat Na(+), K(+)-ATPase, from which the hairpins originate, has a low affinity for ouabain. The low affinity of the rat Na(+),K(+)-ATPase previously had been attributed to the presence of two charged amino acids in the extracellular domain between M1 and M2. In the HN34/56 chimera, the M1/M2 loop, however, originates from H(+),K(+)-ATPase, which has two polar uncharged amino acids on this position. Placement of two charged amino acids in the M1/M2 loop of chimera HN34/56 results in a decreased ouabain affinity. This indicates that although the M1/M2 loop affects the ouabain affinity, binding occurs when the M3/M4 and M5/M6 hairpins of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase are present.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

