Different phosphorylated forms of RNA polymerase II and associated mRNA processing factors during transcription
- PMID: 11018013
- PMCID: PMC316976
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.824700
Different phosphorylated forms of RNA polymerase II and associated mRNA processing factors during transcription
Abstract
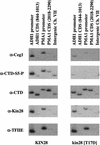
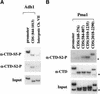
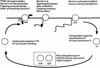
The activities of several mRNA processing factors are coupled to transcription through binding to RNA polymerase II (Pol II). The largest subunit of Pol II contains a repetitive carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) that becomes highly phosphorylated during transcription. mRNA-capping enzyme binds only to phosphorylated CTD, whereas other processing factors may bind to both phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms. Capping occurs soon after transcription initiation and before other processing events, raising the question of whether capping components remain associated with the transcription complex after they have modified the 5' end of the mRNA. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae shows that capping enzyme cross-links to promoters but not coding regions. In contrast, the mRNA cap methyltransferase and the Hrp1/CFIB polyadenylation factor cross-link to both promoter and coding regions. Remarkably, the phosphorylation pattern of the CTD changes during transcription. Ser 5 phosphorylation is detected primarily at promoter regions dependent on TFIIH. In contrast, Ser 2 phosphorylation is seen only in coding regions. These results suggest a dynamic association of mRNA processing factors with differently modified forms of the polymerase throughout the transcription cycle.
Figures
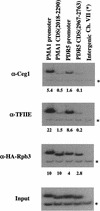

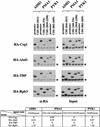
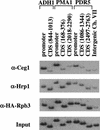
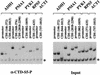
Similar articles
-
Recognition of RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain by 3'-RNA-processing factors.Nature. 2004 Jul 8;430(6996):223-6. doi: 10.1038/nature02679. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15241417
-
Opposing effects of Ctk1 kinase and Fcp1 phosphatase at Ser 2 of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain.Genes Dev. 2001 Dec 15;15(24):3319-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.935901. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11751637 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA capping enzyme is recruited to the transcription complex by phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain.Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 15;11(24):3319-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3319. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9407025 Free PMC article.
-
On the importance of being co-transcriptional.J Cell Sci. 2002 Oct 15;115(Pt 20):3865-71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00073. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12244124 Review.
-
The mRNA assembly line: transcription and processing machines in the same factory.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;14(3):336-42. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(02)00333-2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12067656 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the mediator head module bound to the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):17931-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215241109. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23071300 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of CAP1 in regulation RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription elongation depends on its actin-depolymerization activity in nucleoplasm.Oncogene. 2021 May;40(20):3492-3509. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01789-3. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33911205
-
Quantitative proteomics demonstrates that the RNA polymerase II subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 dissociate during transcriptional elongation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Jun;12(6):1530-8. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.024034. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23418395 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator MED23 regulates basal transcription in vivo via an interaction with P-TEFb.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):39-51. doi: 10.4161/trns.22874. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23340209 Free PMC article.
-
T7 RNA polymerase-directed transcripts are processed in yeast and link 3' end formation to mRNA nuclear export.RNA. 2002 May;8(5):686-97. doi: 10.1017/s1355838202024068. RNA. 2002. PMID: 12022234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cadena DL, Dahmus ME. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:12468–12474. - PubMed
-
- Dahmus M. The role of multisite phosphorylation in the regulation of RNA polymerase II activity. Prog Nucleic Acids Res Mol Biol. 1994;48:143–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
