Protein ligands to HuR modulate its interaction with target mRNAs in vivo
- PMID: 11018049
- PMCID: PMC2189805
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.1.1
Protein ligands to HuR modulate its interaction with target mRNAs in vivo
Abstract
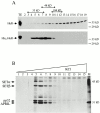
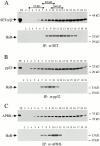
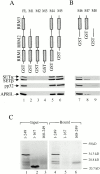
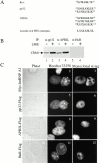
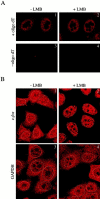
AU-rich elements (AREs) present in the 3' untranslated regions of many protooncogene, cytokine, and lymphokine messages target them for rapid degradation. HuR, a ubiquitously expressed member of the ELAV (embryonic lethal abnormal vision) family of RNA binding proteins, selectively binds AREs and stabilizes ARE-containing mRNAs in transiently transfected cells. Here, we identify four mammalian proteins that bind regions of HuR known to be essential for its ability to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and to stabilize mRNA: SETalpha, SETbeta, pp32, and acidic protein rich in leucine (APRIL). Three have been reported to be protein phosphatase 2A inhibitors. All four ligands contain long, acidic COOH-terminal tails, while pp32 and APRIL share a second motif: rev-like leucine-rich repeats in their NH(2)-terminal regions. We show that pp32 and APRIL are nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins that interact with the nuclear export factor CRM1 (chromosomal region maintenance protein 1). The inhibition of CRM1 by leptomycin B leads to the nuclear retention of pp32 and APRIL, their increased association with HuR, and an increase in HuR's association with nuclear poly(A)+ RNA. Furthermore, transcripts from the ARE-containing c-fos gene are selectively retained in the nucleus, while the cytoplasmic distribution of total poly(A)+ RNA is not altered. These data provide evidence that interaction of its ligands with HuR modulate HuR's ability to bind its target mRNAs in vivo and suggest that CRM1 is instrumental in the export of at least some cellular mRNAs under certain conditions. We discuss the possible role of these ligands upstream of HuR in pathways that govern the stability of ARE-containing mRNAs.
Figures




References
-
- Adler H.T., Nallaseth F.S., Walter G., Tkachuk D.C. HRX leukemic fusion proteins form a heterocomplex with the leukemia-associated protein SET and protein phosphatase 2A. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:28407–28414. - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu W., Okano H.J., Osumi N., Inoue T., Nakamura S., Sakakibara S., Miura M., Matsuo N., Darnell R.B., Okano H. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:9885–9890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson N.G., Maller J.L., Tonks N.K., Sturgill T.W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990;343:651–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

