Regulated interactions between dynamin and the actin-binding protein cortactin modulate cell shape
- PMID: 11018064
- PMCID: PMC2189798
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.1.187
Regulated interactions between dynamin and the actin-binding protein cortactin modulate cell shape
Abstract
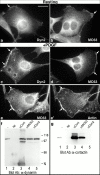
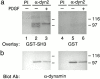
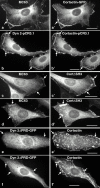
The dynamin family of large GTPases has been implicated in the formation of nascent vesicles in both the endocytic and secretory pathways. It is believed that dynamin interacts with a variety of cellular proteins to constrict membranes. The actin cytoskeleton has also been implicated in altering membrane shape and form during cell migration, endocytosis, and secretion and has been postulated to work synergistically with dynamin and coat proteins in several of these important processes. We have observed that the cytoplasmic distribution of dynamin changes dramatically in fibroblasts that have been stimulated to undergo migration with a motagen/hormone. In quiescent cells, dynamin 2 (Dyn 2) associates predominantly with clathrin-coated vesicles at the plasma membrane and the Golgi apparatus. Upon treatment with PDGF to induce cell migration, dynamin becomes markedly associated with membrane ruffles and lamellipodia. Biochemical and morphological studies using antibodies and GFP-tagged dynamin demonstrate an interaction with cortactin. Cortactin is an actin-binding protein that contains a well defined SH3 domain. Using a variety of biochemical methods we demonstrate that the cortactin-SH3 domain associates with the proline-rich domain (PRD) of dynamin. Functional studies that express wild-type and mutant forms of dynamin and/or cortactin in living cells support these in vitro observations and demonstrate that an increased expression of cortactin leads to a significant recruitment of endogenous or expressed dynamin into the cell ruffle. Further, expression of a cortactin protein lacking the interactive SH3 domain (CortDeltaSH3) significantly reduces dynamin localization to the ruffle. Accordingly, transfected cells expressing Dyn 2 lacking the PRD (Dyn 2(aa)DeltaPRD) sequester little of this protein to the cortactin-rich ruffle. Interestingly, these mutant cells are viable, but display dramatic alterations in morphology. This change in shape appears to be due, in part, to a striking increase in the number of actin stress fibers. These findings provide the first demonstration that dynamin can interact with the actin cytoskeleton to regulate actin reorganization and subsequently cell shape.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

