Disruption of the myocardial extracellular matrix leads to cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 11018073
- PMCID: PMC517818
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8040
Disruption of the myocardial extracellular matrix leads to cardiac dysfunction
Abstract
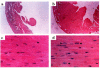
MMP activity with disruption of structural collagen has been implicated in the pathophysiology of dilated cardiomyopathy. To examine the role of this enzyme in cardiac function, a transgenic mouse was created that constitutively expressed human collagenase (MMP-1) in the heart. At 6 months of age, these animals demonstrated compensatory myocyte hypertrophy with an increase in the cardiac collagen concentration due to elevated transcription of type III collagen. Chronic myocardial expression of MMP-1 produced loss of cardiac interstitial collagen coincident with a marked deterioration of systolic and diastolic function at 12 months of age. This is the first animal model demonstrating that direct disruption of the extracellular matrix in the heart reproduces the changes observed in the progression of human heart failure.
Figures






Comment in
-
Matrix metalloproteinases: not-so-innocent bystanders in heart failure.J Clin Invest. 2000 Oct;106(7):827-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI11263. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11018069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Connell JB, Bristow MR. Economic impact of heart failure in the United States: time for a different approach. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1994;13:S107–S112. - PubMed
-
- Katz, A.M. 1992. Heart failure. Raven Press. New York, New York, USA. 200–280.
-
- Weber KT. Cardiac interstitium in health and disease: the fibrillar collagen network. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989;13:1637–1652. - PubMed
-
- Hasenfuss G. Animal models of human cardiovascular disease, heart failure and hypertrophy. Cardiovasc Res. 1998;39:60–76. - PubMed
-
- Franz WM, Mueller OJ, Hartong R, Frey N, Katus HA. Transgenic animal models: new avenues in cardiovascular physiology. J Mol Med. 1997;75:115–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

