G protein modulation of recombinant P/Q-type calcium channels by regulators of G protein signalling proteins
- PMID: 11018106
- PMCID: PMC2270115
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00065.x
G protein modulation of recombinant P/Q-type calcium channels by regulators of G protein signalling proteins
Abstract
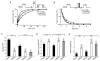
1. Fast synaptic transmission is triggered by the activation of presynaptic Ca2+ channels which can be inhibited by Gbetagamma subunits via G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). Regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins are GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs), which are responsible for >100-fold increases in the GTPase activity of G proteins and might be involved in the regulation of presynaptic Ca2+ channels. In this study we investigated the effects of RGS2 on G protein modulation of recombinant P/Q-type channels expressed in a human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cell line using whole-cell recordings. 2. RGS2 markedly accelerates transmitter-mediated inhibition and recovery from inhibition of Ba2+ currents (IBa) through P/Q-type channels heterologously expressed with the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (mAChR M2). 3. Both RGS2 and RGS4 modulate the prepulse facilitation properties of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. G protein reinhibition is accelerated, while release from inhibition is slowed. These kinetics depend on the availability of G protein alpha and betagamma subunits which is altered by RGS proteins. 4. RGS proteins unmask the Ca2+ channel beta subunit modulation of Ca2+ channel G protein inhibition. In the presence of RGS2, P/Q-type channels containing the beta2a and beta3 subunits reveal significantly altered kinetics of G protein modulation and increased facilitation compared to Ca2+ channels coexpressed with the beta1b or beta4 subunit.
Figures
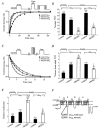

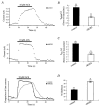

 ) cells are shown with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Time courses of IBa reinhibition were fitted with a single exponential, and mean time constants (τreinhib) ±
) cells are shown with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Time courses of IBa reinhibition were fitted with a single exponential, and mean time constants (τreinhib) ±  ) cells, are shown with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Time courses of IBa release from inhibition were fitted with a single exponential, and mean time constants (τrelease from inhib) ±
) cells, are shown with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Time courses of IBa release from inhibition were fitted with a single exponential, and mean time constants (τrelease from inhib) ±  ) cells, with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Currents were normalized to the largest peak current of the second test pulse versus the first test pulse from the traces in C and D. Numbers of cells tested are indicated in parentheses. * P < 0·05, Student’s t test.
) cells, with Gβ1 subunit or GTPγS in the intracellular solution as indicated. Currents were normalized to the largest peak current of the second test pulse versus the first test pulse from the traces in C and D. Numbers of cells tested are indicated in parentheses. * P < 0·05, Student’s t test.Similar articles
-
Muscarinic stimulation of alpha1E Ca channels is selectively blocked by the effector antagonist function of RGS2 and phospholipase C-beta1.J Neurosci. 2000 Oct 1;20(19):7167-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07167.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11007872 Free PMC article.
-
Gating properties of GIRK channels activated by Galpha(o)- and Galpha(i)-coupled muscarinic m2 receptors in Xenopus oocytes: the role of receptor precoupling in RGS modulation.J Physiol. 2002 Dec 1;545(2):355-73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032151. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12456817 Free PMC article.
-
Differential occurrence of reluctant openings in G-protein-inhibited N- and P/Q-type calcium channels.J Gen Physiol. 2000 Feb;115(2):175-92. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.2.175. J Gen Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10653895 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of ion channels by somatostatin and acetylcholine.Prog Neurobiol. 1992;38(2):203-30. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90040-l. Prog Neurobiol. 1992. PMID: 1372125 Review.
-
[Binding of G alpha o N-terminus is responsible for the voltage-resistant inhibition of alpha 1A (P/Q-type, Cav2.1) Ca2+ channels].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002 Aug;122(8):565-72. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.122.565. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12187771 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
How regulators of G protein signaling achieve selective regulation.J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 16;366(2):349-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.045. Epub 2006 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17173929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin of the voltage dependence of G-protein regulation of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 24;28(52):14176-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1350-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19109500 Free PMC article.
-
Chick RGS2L demonstrates concentration-dependent selectivity for pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive pathways that inhibit L-type Ca2+ channels.J Physiol. 2003 May 15;549(Pt 1):157-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.034439. Epub 2003 Mar 21. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12651916 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstituted slow muscarinic inhibition of neuronal (Ca(v)1.2c) L-type Ca2+ channels.Biophys J. 2002 Dec;83(6):3256-67. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75327-7. Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12496094 Free PMC article.
-
The ß subunit of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.Physiol Rev. 2010 Oct;90(4):1461-506. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00057.2009. Physiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20959621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berman DM, Gilman AG. Mammalian RGS proteins: barbarians at the gate. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998;273:1269–1272. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L, Qin N, Olcese R, Tareilus E, Platano D, Costantin J, Stefani E. Structures and functions of calcium channel β subunits. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 1998;30:357–375. - PubMed
-
- Bünemann M, Hosey MM. Regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins constitutively activate Gβγ-gated potassium channels. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998;273:31186–31190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

