Mechanism of promoter melting by the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group B helicase of transcription factor IIH revealed by protein-DNA photo-cross-linking
- PMID: 11027286
- PMCID: PMC86426
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8168-8177.2000
Mechanism of promoter melting by the xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group B helicase of transcription factor IIH revealed by protein-DNA photo-cross-linking
Abstract
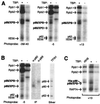
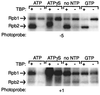
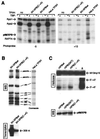
The p89/xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group B (XPB) ATPase-helicase of transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is essential for promoter melting prior to transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). By studying the topological organization of the initiation complex using site-specific protein-DNA photo-cross-linking, we have shown that p89/XPB makes promoter contacts both upstream and downstream of the initiation site. The upstream contact, which is in the region where promoter melting occurs (positions -9 to +2), requires tight DNA wrapping around RNAPII. The addition of hydrolyzable ATP tethers the template strand at positions -5 and +1 to RNAPII subunits. A mutation in p89/XPB found in a xeroderma pigmentosum patient impairs the ability of TFIIH to associate correctly with the complex and thereby melt promoter DNA. A model for open complex formation is proposed.
Figures




References
-
- Bagby S, Kim S J, Maldonado E, Tong K I, Reinberg D, Ikura M. Solution structure of the C-terminal core domain of human TFIIB: similarity to cyclin A and interaction with TATA-binding protein. Cell. 1995;82:857–867. - PubMed
-
- Conaway J W, Conaway R C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:2357–2362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
