Human scribble (Vartul) is targeted for ubiquitin-mediated degradation by the high-risk papillomavirus E6 proteins and the E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase
- PMID: 11027293
- PMCID: PMC86433
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.21.8244-8253.2000
Human scribble (Vartul) is targeted for ubiquitin-mediated degradation by the high-risk papillomavirus E6 proteins and the E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase
Abstract
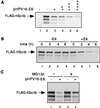
The high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 proteins stimulate the ubiquitination and degradation of p53, dependent on the E6AP ubiquitin-protein ligase. Other proteins have also been shown to be targeted for degradation by E6, including hDlg, the human homolog of the Drosophila melanogaster Discs large (Dlg) tumor suppressor. We show here that the human homolog of the Drosophila Scribble (Vartul) (hScrib) tumor suppressor protein is also targeted for ubiquitination by the E6-E6AP complex in vitro and that expression of E6 induces degradation of hScrib in vivo. Characterization of the E6AP-E6-hScrib complex indicated that hScrib binds directly to E6 and that the binding is mediated by the PDZ domains of hScrib and a carboxyl-terminal epitope conserved among the high-risk HPV E6 proteins. Green fluorescent protein-hScrib was localized to the periphery of MDCK cells, where it colocalized with ZO-1, a component of tight junctions. E6 expression resulted in loss of integrity of tight junctions, as measured by ZO-1 localization, and this effect was dependent on the PDZ binding epitope of E6. Thus, the high-risk HPV E6 proteins induce the degradation of the human homologs of two Drosophila PDZ domain-containing tumor suppressor proteins, hDlg and hScrib, both of which are associated with cell junction complexes. The fact that Scrib/Vart and Dlg appear to cooperate in a pathway that controls Drosophila epithelial cell growth suggests that the combined targeting of hScrib and hDlg is an important component of the biologic activity of high-risk HPV E6 proteins.
Figures







References
-
- Bilder D, Perrimon N. Localization of apical determinants by the basolateral PDZ protein Scribble. Nature. 2000;403:676–680. - PubMed
-
- Bilder D, Li M, Perrimon N. Cooperative regulation of cell polarity and growth by Drosophila tumor suppressors. Science. 2000;289:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Bilder D, Birnbaum D, Borg J-P, Bryant P, Huibregtse J M, Jansen E, Kennedy M B, Labouesse M, Legouis R, Mechler B, Perrimon N, Petit M, Sinha P. Collective nomenclature for LAP proteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:E114. - PubMed
-
- Chen J J, Hong Y, Androphy E J. Mutational analysis of transcriptional activation by the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E6. Virology. 1997;236:30–36. - PubMed
-
- Crook T, Tidy J A, Vousden K H. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991;67:547–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
