Global mapping of meiotic recombination hotspots and coldspots in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11027339
- PMCID: PMC17209
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.21.11383
Global mapping of meiotic recombination hotspots and coldspots in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
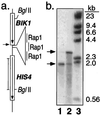
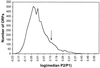
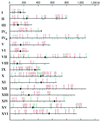
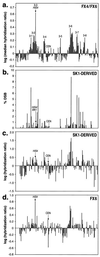
In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, meiotic recombination is initiated by double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs). Meiotic DSBs occur at relatively high frequencies in some genomic regions (hotspots) and relatively low frequencies in others (coldspots). We used DNA microarrays to estimate variation in the level of nearby meiotic DSBs for all 6,200 yeast genes. Hotspots were nonrandomly associated with regions of high G + C base composition and certain transcriptional profiles. Coldspots were nonrandomly associated with the centromeres and telomeres.
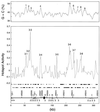
Figures
References
-
- Lichten M, Goldman A S. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:423–444. - PubMed
-
- Petes T D, Malone R E, Symington L S. In: The Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces. Broach J, Jones E W, Pringle J R, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1991. pp. 407–521.
-
- Wu T C, Lichten M. Science. 1994;263:515–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

