Specific Th2 cells accumulate in the central nervous system of mice protected against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by copolymer 1
- PMID: 11027347
- PMCID: PMC17224
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.21.11472
Specific Th2 cells accumulate in the central nervous system of mice protected against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by copolymer 1
Abstract
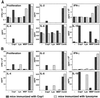
This study addresses the issue of the effect of immunomodulating therapies in the target organ-the central nervous system (CNS)-in the case of multiple sclerosis. Copolymer 1 (Cop 1, Copaxone, glatiramer acetate), an approved drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis, is a potent inducer of Th2 regulatory cells in both mice and humans. Highly reactive Cop 1-specific T cell lines that secrete IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, and transforming growth factor-beta in response to Cop 1 and crossreact with myelin basic protein (MBP) at the level of Th2 cytokine secretion were established from both brains and spinal cords of Cop 1-treated mice. In contrast, no reactivity to the control antigen lysozyme could be obtained in lymphocytes isolated from CNS of mice injected with lysozyme. Adoptively transferred labeled Cop 1-specific suppressor cells were found in brain sections 7 and 10 days after their injection to the periphery, whereas lysozyme-specific cells were absent in the CNS. Hence, Cop 1-induced Th2 cells cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in the CNS, where they can be stimulated in situ by MBP and thereby exert therapeutic effects in the diseased organ. This therapeutic effect was manifested, in brains of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced mice, by a decrease in the inflammatory cytokine interferon-gamma and by secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in response to the autoantigen MBP.
Figures



References
-
- Wekerle H, Linington C, Lassmann H, Meyermann R. Trends Neurosci. 1986;9:271–277.
-
- Cross A H, O'Mara T, Raine C S. Neurology. 1993;43:1028–1033. - PubMed
-
- Wekerle H. Lab Invest. 1984;51:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum D, Aharoni R, Fridkis-Hareli M, Arnon R, Sela M. In: The Decade in Autoimmunity. Shoenfeld Y, editor. New York: Elsevier; 1998. pp. 183–188.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

