Characterization of Arabidopsis acid phosphatase promoter and regulation of acid phosphatase expression
- PMID: 11027712
- PMCID: PMC59168
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.2.615
Characterization of Arabidopsis acid phosphatase promoter and regulation of acid phosphatase expression
Abstract
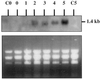
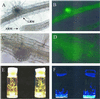
The expression and secretion of acid phosphatase (APase) was investigated in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.) plants using sensitive in vitro and activity gel assays. Phosphorus (P) starvation induced two APases in Indian mustard roots, only one of which was secreted. Northern-blot analysis indicated transcriptional regulation of APase expression. Polymerase chain reaction and Southern-blot analyses revealed two APase homologs in Indian mustard, whereas in Arabidopsis, only one APase homolog was detected. The Arabidopsis APase promoter region was cloned and fused to the beta-glucuronidase (GUS) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter genes. GUS expression was first evident in leaves of the P-starved Arabidopsis plants. In P-starved roots, the expression of GUS initiated in lateral root meristems followed by generalized expression throughout the root. GUS expression diminished with the addition of P to the medium. Expression of GFP in P-starved roots also initiated in the lateral root meristems and the recombinant GFP with the APase signal peptide was secreted by the roots into the medium. The APase promoter was specifically activated by low P levels. The removal of other essential elements or the addition of salicylic or jasmonic acids, known inducers of gene expression, did not activate the APase promoter. This novel APase promoter may be used as a plant-inducible gene expression system for the production of recombinant proteins and as a tool to study P metabolism in plants.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The promoter of the nematode resistance gene Hs1pro-1 activates a nematode-responsive and feeding site-specific gene expression in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) and Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 Jun;52(3):643-60. doi: 10.1023/a:1024887516581. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12956533
-
Molecular characterization of a Phi-class mustard (Brassica juncea) glutathione S-transferase gene in Arabidopsis thaliana by 5'-deletion analysis of its promoter.Plant Cell Rep. 2005 Sep;24(7):439-47. doi: 10.1007/s00299-005-0961-9. Epub 2005 May 31. Plant Cell Rep. 2005. PMID: 15926064
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana ACT4/ACT12 actin gene subclass is strongly expressed throughout pollen development.Plant J. 1996 Aug;10(2):189-202. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1996.10020189.x. Plant J. 1996. PMID: 8771777
-
The THO/TREX Complex Active in miRNA Biogenesis Negatively Regulates Root-Associated Acid Phosphatase Activity Induced by Phosphate Starvation.Plant Physiol. 2016 Aug;171(4):2841-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00680. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27329222 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of a novel Athspr promoter specifically active in vascular tissue.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 May;78:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24675528
Cited by
-
Transcriptional responses of maize seedling root to phosphorus starvation.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Sep;40(9):5359-79. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2636-x. Epub 2013 May 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23670044
-
Transcripts of MYB-like genes respond to phosphorous and nitrogen deprivation in Arabidopsis.Planta. 2004 Oct;219(6):1003-9. doi: 10.1007/s00425-004-1305-7. Epub 2004 Jun 25. Planta. 2004. PMID: 15592750
-
Molecular control of acid phosphatase secretion into the rhizosphere of proteoid roots from phosphorus-stressed white lupin.Plant Physiol. 2001 Oct;127(2):594-606. Plant Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11598233 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in Trichoderma harzianum antagonism of fungal plant pathogens by secreted protein analysis.Curr Microbiol. 2010 Oct;61(4):298-305. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9611-8. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Curr Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20213103
-
The Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase AtPAP10 is predominantly associated with the root surface and plays an important role in plant tolerance to phosphate limitation.Plant Physiol. 2011 Nov;157(3):1283-99. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.183723. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21941000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoyama T, Chua NH. A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 1997;11:605–612. - PubMed
-
- Arnon DI, Hoagland DR. Crop production in artificial culture solutions and in soils with special reference to factors influencing yields and absorption of inorganic nutrients. Soil Sci. 1940;50:463–483.
-
- Ascencio J. Root secreted acid phosphatase kinetics as a physiological marker for phosphorus deficiency. J Plant Nutr. 1997;20:9–26.
-
- Basha SM. Purification and characterization of an acid phosphatase from peanut (Arachis hypogaea) seed. Can J Bot. 1983;62:385–391.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

