The diabetes autoantigen ICA69 and its Caenorhabditis elegans homologue, ric-19, are conserved regulators of neuroendocrine secretion
- PMID: 11029035
- PMCID: PMC14991
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.10.3277
The diabetes autoantigen ICA69 and its Caenorhabditis elegans homologue, ric-19, are conserved regulators of neuroendocrine secretion
Abstract
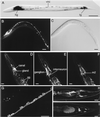
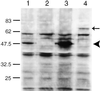
ICA69 is a diabetes autoantigen with no homologue of known function. Given that most diabetes autoantigens are associated with neuroendocrine secretory vesicles, we sought to determine if this is also the case for ICA69 and whether this protein participates in the process of neuroendocrine secretion. Western blot analysis of ICA69 tissue distribution in the mouse revealed a correlation between expression levels and secretory activity, with the highest expression levels in brain, pancreas, and stomach mucosa. Subcellular fractionation of mouse brain revealed that although most of the ICA69 pool is cytosolic and soluble, a subpopulation is membrane-bound and coenriched with synaptic vesicles. We used immunostaining in the HIT insulin-secreting beta-cell line to show that ICA69 localizes in a punctate manner distinct from the insulin granules, suggesting an association with the synaptic-like microvesicles found in these cells. To pursue functional studies on ICA69, we chose to use the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, for which a homologue of ICA69 exists. We show that the promoter of the C. elegans ICA69 homologue is specifically expressed in all neurons and specialized secretory cells. A deletion mutant was isolated and found to exhibit resistance to the drug aldicarb (an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase), suggesting defective neurotransmitter secretion in the mutant. On the basis of the aldicarb resistance phenotype, we named the gene ric-19 (resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase-19). The resistance to aldicarb was rescued by introducing a ric-19 transgene into the ric-19 mutant background. This is the first study aimed at dissecting ICA69 function, and our results are consistent with the interpretation that ICA69/RIC-19 is an evolutionarily conserved cytosolic protein participating in the process of neuroendocrine secretion via association with certain secretory vesicles.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson GL. Responses of dauer larvae of Caenorhabditis elegans (Nematoda:Rhabditidae) to thermal stress and oxygen deprivation. Can J Zool. 1978;56:1786–1791.
-
- Avery L. Motor neuron M3 controls pharyngeal muscle relaxation timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Exp Biol. 1993;175:283–297. - PubMed
-
- Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot H, Christgau S, Reetz A, Solimena M, Cascalho M, Folli F, Richter-Olsen H, De Camilli P. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990;347:151–156. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Harwieg E, Horvitz HR. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;74:515–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

