A second allele of eppA in Borrelia burgdorferi strain B31 is located on the previously undetected circular plasmid cp9-2
- PMID: 11029452
- PMCID: PMC94766
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.21.6254-6258.2000
A second allele of eppA in Borrelia burgdorferi strain B31 is located on the previously undetected circular plasmid cp9-2
Abstract
Although sequence analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolate B31 was recently declared "complete," we found that cultures of this strain can contain a novel 9-kb circular plasmid, cp9-2. The newly described plasmid contains both sequence similarities with and differences from the previously identified B31 plasmid cp9-1 (formerly cp9). cp9-1 and cp9-2 each encode a unique allele of EppA, a putative membrane protein synthesized by B. burgdorferi during mammalian infection.
Figures

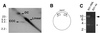

References
-
- Barbour A G, Burgdorfer W, Hayes S F, Peter O, Aeschlimann A. Isolation of a cultivable spirochete from Ixodes ricinus ticks of Switzerland. Curr Microbiol. 1983;8:123–126.
-
- Barbour A G, Garon C F. The genes encoding major surface proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi are located on a plasmid. In: Benach J L, Bosler E M, editors. Lyme disease and related disorders. New York, N.Y: New York Academy of Sciences; 1988. pp. 144–153. - PubMed
-
- Bergström S, Garon C F, Barbour A G, MacDougall J. Extrachromosomal elements of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992;143:623–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

