Neuroprotective abilities of resveratrol and other red wine constituents against nitric oxide-related toxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 11030720
- PMCID: PMC1572384
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703626
Neuroprotective abilities of resveratrol and other red wine constituents against nitric oxide-related toxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons
Abstract
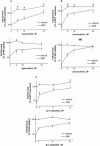
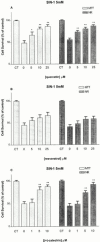
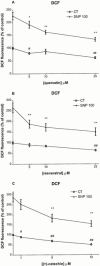
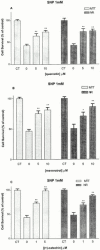
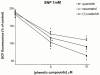
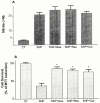
Animal and epidemiological studies suggest that polyphenol constituents of red wine possess antioxidant activities that favour protection against cardiovascular disease - the so-called. 'French paradox' - and possibly, central nervous system disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and ischaemia. In the present study, the potential of three major red wine derived-polyphenols to protect against toxicity induced by the nitric oxide free radical donors sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1) was examined in cultured rat hippocampal cells. Both co- and post-treatments with either the stilbene resveratrol (5 - 25 microM) or the flavonoids quercetin (5 - 25 microM) and (+)-catechin (1 - 10 microM) were capable of attenuating hippocampal cell death and intracellular reactive oxygen species accumulation produced by SNP (100 microM and 1 mM, respectively). However, among the phenolic compounds tested, only the flavonoids afforded significant protection against 5 mM SIN-1-induced toxicity. The effects of phenolic constituents were shared by Trolox (100 microM), a vitamin E analogue, but not by selective inhibitors of cyclo-oxygenases (COX) and lipoxygenases (LOX). Among the phenolic compounds tested, only quercetin (10 microM) inhibited 100 microM SNP-stimulated protein kinase C (PKC) activation, whereas none of them were able to attenuate nitrite accumulation caused by SNP (100 microM). Taken together, these data suggest that the neuroprotective abilities of quercetin, resveratrol, and (+)-catechin result from their antioxidant properties rather than their purported inhibitory effects on intracellular enzymes such as COX, LOX, or nitric oxide synthase. Quercetin, however, may also act via PKC to produce its protective effects.
Figures

References
-
- BASTIANETTO S., ZHENG W.H., QUIRION R. The ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects and rescues hippocampal cells against nitric oxide-induced toxicity: involvement of its flavonoid constituents and protein kinase C. J. Neurochem. 2000;74:2268–2277. - PubMed
-
- BELGUENDOUZ L., FREMONT L., LINARD A. Resveratrol inhibits metal ion-dependent and independent peroxidation of porcine low-density lipoproteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997;53:1347–1355. - PubMed
-
- BERTELLI A., BERTELLI A.A., GOZZINI A., GIOVANNINI L. Plasma and tissue resveratrol concentrations and pharmacological activity. Drugs Under Exp. Clin. Res. 1998;24:133–138. - PubMed
-
- BERTELLI A.A., GIOVANNINI L., STRADI R., URIEN S., TILLEMENT J.P., BERTELLI A. Kinetics of trans- and cis-resveratrol (3,4′,5-trihydroxystilbene) after red wine oral administration in rats. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Res. 1996;16:77–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

