X-ray crystal structure of rabbit N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I: catalytic mechanism and a new protein superfamily
- PMID: 11032794
- PMCID: PMC314010
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5269
X-ray crystal structure of rabbit N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I: catalytic mechanism and a new protein superfamily
Abstract
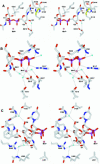
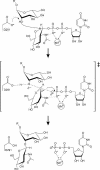
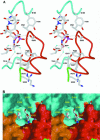
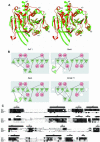
N:-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (GnT I) serves as the gateway from oligomannose to hybrid and complex N:-glycans and plays a critical role in mammalian development and possibly all metazoans. We have determined the X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic fragment of GnT I in the absence and presence of bound UDP-GlcNAc/Mn(2+) at 1.5 and 1.8 A resolution, respectively. The structures identify residues critical for substrate binding and catalysis and provide evidence for similarity, at the mechanistic level, to the deglycosylation step of retaining beta-glycosidases. The structuring of a 13 residue loop, resulting from UDP-GlcNAc/Mn(2+) binding, provides an explanation for the ordered sequential 'Bi Bi' kinetics shown by GnT I. Analysis reveals a domain shared with Bacillus subtilis glycosyltransferase SpsA, bovine beta-1,4-galactosyl transferase 1 and Escherichia coli N:-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. The low sequence identity, conserved fold and related functional features shown by this domain define a superfamily whose members probably share a common ancestor. Sequence analysis and protein threading show that the domain is represented in proteins from several glycosyltransferase families.
Figures
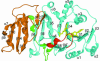

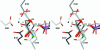
References
-
- Artymiuk P.J., Rice,D.W., Poirrette,A.R. and Willett,P. (1995) β-Glucosyltransferase and phosphorylase reveal their common theme. Nature Struct. Biol., 2, 117–120. - PubMed
-
- Bacon D.J. and Anderson,W.F. (1988) A fast algorithm for rendering space-filling molecule pictures. J. Mol. Graph., 6, 219–220.
-
- Barton G.J. (1993) ALSCRIPT a tool to format multiple sequence alignments. Protein Eng., 6, 37–40. - PubMed
-
- Black C.B., Huang,H.-W. and Cowan,J.A. (1994) Biological coordination chemistry of magnesium, sodium, and potassium ions. Protein and nucleotide binding sites. Coord. Chem. Rev., 135/136, 165–202.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

