Activation of B-Raf kinase requires phosphorylation of the conserved residues Thr598 and Ser601
- PMID: 11032810
- PMCID: PMC314015
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5429
Activation of B-Raf kinase requires phosphorylation of the conserved residues Thr598 and Ser601
Abstract
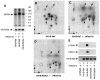
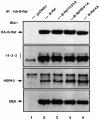
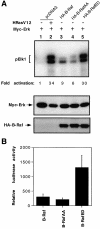
The Raf kinase family serves as a central intermediate to relay signals from Ras to ERK. The precise molecular mechanism for Raf activation is still not fully understood. Here we report that phosphorylation of Thr598 and Ser601, which lie between kinase subdomains VII and VIII, is essential for B-Raf activation by Ras. Substitution of these residues by alanine (B-RafAA) abolished Ras-induced B-Raf activation without altering the association of B-Raf with other signaling proteins. Phosphopeptide mapping and immunoblotting with phospho-specific antibodies confirmed that Thr598 and Ser601 are in vivo phosphorylation sites induced by Ras. Furthermore, replacement of these two sites by acidic residues (B-RafED) renders B-Raf constitutively active. Con sistent with these data, B-RafAA and B-RafED exhibited diminished and enhanced ability, respectively, to stimulate ERK activation and Elk-dependent transcription. Moreover, functional studies revealed that B-RafED was able to promote NIH 3T3 cell transformation and PC12 cell differentiation. Since Thr598 and Ser601 are conserved in all Raf family members from Caenorhabditis elegans to mammals, we propose that phosphorylation of these two residues may be a general mechanism for Raf activation.
Figures





References
-
- Alessi D.R. and Cohen,P. (1998) Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 8, 55–62. - PubMed
-
- Carroll M.P. and May,W.S. (1994) Protein kinase C-mediated serine phosphorylation directly activates Raf-1 in murine hematopoietic cells. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 1249–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

