Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation
- PMID: 11032855
- PMCID: PMC314347
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10905
Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation
Abstract
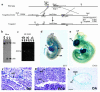
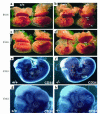
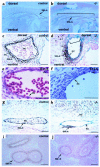
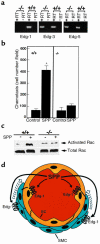
Sphingolipid signaling pathways have been implicated in many critical cellular events. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (SPP), a sphingolipid metabolite found in high concentrations in platelets and blood, stimulates members of the endothelial differentiation gene (Edg) family of G protein-coupled receptors and triggers diverse effects, including cell growth, survival, migration, and morphogenesis. To determine the in vivo functions of the SPP/Edg signaling pathway, we disrupted the Edg1 gene in mice. Edg1(-/-) mice exhibited embryonic hemorrhage leading to intrauterine death between E12.5 and E14.5. Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis appeared normal in the mutant embryos. However, vascular maturation was incomplete due to a deficiency of vascular smooth muscle cells/pericytes. We also show that Edg-1 mediates an SPP-induced migration response that is defective in mutant cells due to an inability to activate the small GTPase, Rac. Our data reveal Edg-1 to be the first G protein-coupled receptor required for blood vessel formation and show that sphingolipid signaling is essential during mammalian development.
Figures

Comment in
-
A new role of lipid receptors in vascular and cardiac morphogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2000 Oct;106(8):939-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI11304. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11032853 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Shayman JA. Perspectives in basic science: sphingolipids. Kidney Int. 2000;58:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Huwiler A, Kolter T, Pfeilschifter J, Sandhoff K. Physiology and pathophysiology of sphingolipid metabolism and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1485:63–99. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel S, Merrill AH., Jr Sphingolipid metabolism and cell growth regulation. FASEB J. 1996;10:1388–1397. - PubMed
-
- Lee MJ, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science. 1998;279:1552–1555. - PubMed
-
- Hla T, Maciag T. An abundant transcript induced in differentiating human endothelial cells encodes a polypeptide with structural similarities to G-protein–coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:9308–9313. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

