Corticosteroids or ACTH for acute exacerbations in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 11034713
- PMCID: PMC11391333
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001331
Corticosteroids or ACTH for acute exacerbations in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Corticosteroids are often used to improve the rate of recovery from acute exacerbation in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. However, it is still unclear just how relatively effective these agents are and the type of drug, optimal dose, frequency, duration of treatment and route of administration are unknown.
Objectives: The object of this review was to determine the efficacy and safety of corticosteroids or ACTH in reducing the short and long term morbidity from MS. Moreover, we wished to examine from indirect comparisons if the effect of corticosteroids is different according to different doses and drugs, routes of administration, length of treatment.
Search strategy: A search strategy developed for the Cochrane MS Group (last searched: June 1999) completed with handsearching and personal contacts with trialists and pharmaceutical companies was used.
Selection criteria: All randomised, double-blind, unconfounded trials comparing corticosteroids or ACTH to placebo in patients with MS, treated for acute exacerbations, without any age or severity restrictions, were evaluated.
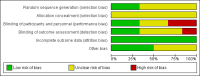
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently selected articles for inclusion, assessed trials' quality and extracted the data. A third reviewer cross-checked them and disagreements were resolved by a joint discussion.
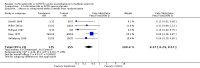
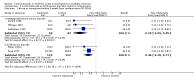
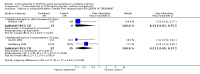
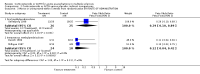
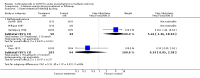
Main results: Six trials contributed to this review; a total of 377 participants (199 treatment, 178 placebo) were randomised. The drugs analysed were methylprednisolone (MP) (four trials, 140 patients) and ACTH (two trials, 237 patients). Overall, MP or ACTH showed a protective effect against the disease getting worse or stable within the first five weeks of treatment (odds ratio[OR]=0.37, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.24-0.57) with some but non significant greater effect for MP and intravenous administration. Short (five days) or long (15 days) duration of treatment with MP did not show any significant difference. Only one study (with 51 patients) reported data after one year of follow-up: no difference between oral MP and placebo in the prevention of new exacerbations or improvement in long term disability was detected. No data are available beyond one year of follow-up to indicate whether steroids or ACTH have any effect on long-term progression. One study reported that a short term treatment with high dose intravenous MP was not attended by adverse events. On the contrary, gastrointestinal symptoms and psychic disorders were significantly more common in the oral, high-dose MP than in the placebo group. Weight gain and edema were significantly more frequent in the ACTH group than in controls.
Reviewer's conclusions: We found evidence favouring the corticosteroid MP for acute exacerbation in MS patients. Data are insufficient to reliably estimate effect of corticosteroids on prevention of new exacerbations and reduction of long-term disability. Studies assessing long term risk/benefit and adverse effects of corticosteroids in MS patients are urgently needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures







References
References to studies included in this review
Durelli 1986 {published data only}
-
- Durelli L, Baggio GF, Bergamasco B, Barile C, Cocito D, Delsedime M, et al. Early immunosuppressive effect of parenteral methylprednisolone in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica 1985;7(3‐4):338‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Durelli L, Cocito D, Riccio A, Barile C, Bergamasco B, Baggio GF, et al. High‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: clinical‐immunologic correlations. Neurology 1986;36(2):238‐43. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Filipovic 1997 {published data only}
-
- Filipovic SR, Drulovic J, Stojsavljevic N, Levic Z. The effects of high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone on event‐related potentials in patients with multiple sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1997;152(2):147‐53. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1997368770] - PubMed
Miller 1961a {published data only}
-
- Miller H, Newell DJ, Ridley A. Treatment of acute exacerbations with corticotrophin (A.C.T.H.). Lancet 1961;2:1120‐2. - PubMed
Milligan 1987 {published data only}
Rose 1970 {published data only}
-
- Rose AS, Kuzma JW, Kurtzke JF, Namerow NS, Sibley WA, Tourtellotte WW. Cooperative study in the evaluation of therapy in multiple sclerosis. ACTH vs. placebo. Final report. Neurology 1970;20(5 Part 2):1‐59. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rose AS, Kuzma JW, Kurtzke JF, Sibley WA, Tourtellotte WW. Cooperative study in the evaluation of therapy in multiple sclerosis; ACTH vs. placebo in acute exacerbations. Preliminary report. Neurology 1968;18(Suppl 6):1‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sellebjerg 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sellebjerg F, Frederiksen JL, Nielsen PM, Olesen J. Double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study of oral, high‐dose methylprednisolone in attacks of MS. Neurology 1998;51(2):529‐34. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1998298663] - PubMed
-
- Sellebjerg F, Frederiksen JL, Nielsen PM, Olesen J. Randomized controlled trial of high‐dose peroral methylprednisolone in attacks of multiple sclerosis. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1999;161(48):6625‐9. - PubMed
-
- Sellebjerg F, Jensen CV, Larsson HB, Frederiksen JL. Gadolinium‐enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predicts response to methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 2003;9(1):102‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Barkhof 1991 {published data only}
-
- Barkhof F, Hommes OR, Scheltens P, Valk J. Quantitative MRI changes in gadolinium‐DTPA enhancement after high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1991;41(8):1219‐22. - PubMed
Beretta 1997 {published data only}
-
- Beretta S, Checcarelli N, Manfredi L, Adobbati L, Garavaglia P, Guidotti M, et al. [Efficacia del trattamento con ripetute megadosi di metilprednisolone nella profilassi delle ricadute nella sclerosi multipla tipo relapsing‐remitting]. XXXVII Congresso Nazionale della Società dei Neurologi Neurochirurghi e Neuroradiologi Ospedalieri S.N.O. Como, 1997:37‐8.
Boman 1966 {published data only}
-
- Boman K, Hokkanen E, Jarho L, Kivalo E. Double‐blind study of the effect of corticotropin treatment in multiple sclerosis. Annales Medicinae Internae Fenniae 1966;55(3):71‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Buckley 1982 {published data only}
Burnham 1991 {published data only}
-
- Burnham JA, Wright RR, Dreisbach J, Murray RS. The effect of high‐dose steroids on MRI gadolinium enhancement in acute demyelinating lesions. Neurology 1991;41(9):1349‐54. - PubMed
Ciccone 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ciccone A, Beretta S, Pellegrini G, BPSM (Boli Steroidei Preventivi nella Sclerosi Multipla) Group. Periodic intravenous methylprednisolone megadoses to prevent relapses in multiple sclerosis. Data on file.
Compston 1987 {published data only}
Dong 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dong Y, Li LL, Li YX. Clinical application of different protocols of glucocorticoids on treating multiple sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Neurology 2012;25:144‐6.
Dowling 1980 {published data only}
-
- Dowling PC, Bosch VV, Cook SD. Possible beneficial effect of high‐dose intravenous steroid therapy in acute demyelinating disease and transverse myelitis. Neurology 1980;30(7):33‐6. - PubMed
Frequin 1993 {published data only}
-
- Frequin ST, Wevers RA, Braam M, Barkhof F, Hommes OR. Decreased vitamin B12 and folate levels in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of multiple sclerosis patients after high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Journal of Neurology 1993;240(5):305‐8. - PubMed
Frequin 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frequin ST, Lamers KJ, Barkhof F, Borm GF, Hommes OR. Follow‐up study of MS patients treated with high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1994;90(2):105‐10. - PubMed
Goodkin 1998 {published data only}
-
- Goodkin DE, Kinkel RP, Weinstock‐Guttman B, VanderBrug‐Medendorp S, Secic M, Gogol D, et al. A phase II study of i.v. methylprednisolone in secondary‐progressive multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1998;51(1):239‐45. - PubMed
Gunal 1996 {published data only}
-
- Gunal D, Tekin S, Tanridag T, Aktan S. The effect of methylprednisolone on the disease progression in multiple sclerosis. European Journal of Neurology 1996;3:59.
Hoogervorst 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hoogervorst EL, Polman CH, Barkhof F. Cerebral volume changes in multiple sclerosis patients treated with high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Multiple Sclerosis 2002;8(5):415‐9. - PubMed
Hoogstraten 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hoogstraten MC, Minderhoud JM. Long‐term effect of ACTH treatment of relapse in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1990;82(1):74‐7. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1990255121] - PubMed
Kesselring 1989 {published data only}
Kiessling 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kiessling, W. Transdermal effects of a synthetic alpha‐melanotropin/corticotropin analog in multiple sclerosis. Archives of Neurology 1987;44:995. - PubMed
Kupersmith 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kupersmith MJ, Kaufman D, Paty DW, Ebers G, McFarland H, Johnson K, et al. Megadose corticosteroids in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1994;44(1):1‐4. - PubMed
Marforio 1984 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Marforio S. ACTH 1‐17 effects in multiple sclerosis. La Ricerca in Clinica e in Laboratorio 1984;14(2):253‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Martin 1964 {published data only}
-
- Martin E, Kirker J. A controlled trial of ACTH in multiple sclerosis. Journal of the Irish Medical Association 1964;54:146‐49. - PubMed
Martinez‐Caceres 2002 {published data only}
-
- Martinez‐Caceres EM, Barrau MA, Brieva L, Espejo C, Barbera N, Montalban X. Treatment with methylprednisolone in relapses of multiple sclerosis patients: immunological evidence of immediate and short‐term but not long‐lasting effects. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 2002;127(1):165‐71. - PMC - PubMed
Merritt 1954 {published data only}
-
- Merrit HH, Glaser GH, Herrmann C. A study of the short‐ and long‐term effects of adrenal steroids on the clinical patterns of multiple sclerosis. Annals New York Academy of Sciences 1954;58:625‐32.
Millar 1967 {published data only}
-
- Millar JHD, Vas CJ, Noronha MJ, Liversedge LA, Rawson MD. Long‐term treatment of multiple sclerosis with corticotrophin. The Lancet 1967;2(7513):429‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Miller 1961b {published data only}
-
- Miller H, Newell DJ, Ridley A. Trials of maintenance treatment with prednisolone and soluble aspirin. The Lancet 1961;1:127‐9. - PubMed
Miller 1992 {published data only}
Newman 1982 {published data only}
Repovic 2004 {published data only}
-
- Repovic P, Lublin FD. Treatment of multiple sclerosis exacerbations. Neurologic Clinics 2011;29(2):389‐400. - PubMed
Rinne 1968 {published data only}
-
- Rinne UK, Sonninen V, Tuovinen T. Corticotrophin treatment in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1968;44(2):207‐18. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rumbach 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rumbach L, Dietemann JL, Tranchant C, Bodiguel E, Warter JM, Collard M. Magnetic resonance imaging after a one‐month interval of lesions of multiple sclerosis in 2 populations, one during an acute attack treated with methylprednisolone, the other stable with no treatment. Revue Neurologique 1990;146(6‐7):430‐3. - PubMed
Schweingruber 2011 {published data only}
-
- Schweingruber A, Reichardt SD, Reichardt HM. Mechanisms of glucocorticoids in control of neuroinflammation. Journal of Neuroendocrinology 2011;24:174‐82. - PubMed
Sellebjerg 1999b {published data only}
-
- Sellebjerg F, Nielsen HS, Frederiksen JL, Olesen J. A randomized, controlled trial of oral high‐dose methylprednisolone in acute optic neuritis. Neurology 1999;52(7):1479‐84. - PubMed
Then Bergh 2001 {published data only}
-
- Then Bergh F, Kumpfel T, Grasser A, Rupprecht R, Holsboer F, Trenkwalder C. Combined treatment with corticosteroids and moclobemide favours normalization of hypothalamo‐pituitary‐adrenal axis dysregulation in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: a randomized, double blind trial. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2001;86(4):1610‐5. - PubMed
Tourtellotte 1965 {published data only}
-
- Tourtellotte WW, Haerer AF, Arbor A. Use of an oral corticosteroid in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. A double‐blind study. Archives of Neurology 1965;12:536‐45. - PubMed
Tourtellotte 1980 {published data only}
-
- Tourtellotte WW, Baumhefner RW, Potvin AR, Ma BI, Potvin JH, Mendez M, et al. Multiple sclerosis de novo CNS IgG synthesis: effect of ACTH and corticosteroids. Neurology 1980;30(11):1155‐62. - PubMed
Trotter 1980 {published data only}
-
- Trotter JL, Garvey WF. Prolonged effects of large‐dose methylprednisolone infusion in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1980;30(7):702‐8. - PubMed
Versino 1994 {published data only}
-
- Versino M, Bergamaschi R, Callieco R, Romani A, Castelnovo G, Beltrami G, et al. Eye movement quantitative evaluation before and after high‐dose 6‐methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1994;89(2):105‐10. - PubMed
Visser 2004 {published data only}
-
- Visser LH, Beekman R, Tijssen CC, Uitdehaag BM, Lee ML, Movig KL, et al. .A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled pilot study of i.v. immune globulins in combination with i.v. methylprednisolone in the treatment of relapses in patients with MS. Multiple Sclerosis 2004;10(1):89‐91. - PubMed
Whitaker 1993 {published data only}
-
- Whitaker JN, Layton BA, Herman PK, Kachelhofer RD, Burgard S, Bartolucci AA. Correlation of myelin basic protein‐like material in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients with their response to glucocorticoid treatment. Annals of Neurology 1993;33(1):10‐7. - PubMed
Zivadinov 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zivadinov R, Rudick RA, Masi R, Nasuelli D, Ukmar M, Pozzi‐Mucelli RS, et al. Effects of IV methylprednisolone on brain atrophy in relapsing‐remitting MS. Neurology 2001;57(7):1239‐47. - PubMed
Additional references
Atalay 2005
-
- Atalay K, Diren HB, Gelmez S, Incesu L, Terzi M. The effectiveness of magnetization transfer technique in the evaluation of acute plaques in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients and its correlation with the clinical findings. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology 2005;11(3):137‐41. - PubMed
Barkhof 1992
-
- Barkhof R, Frequin ST, Hommes OR, Lamers K, Scheltens Ph, Geel WJ, et al. A correlative triad of gadolinium‐DTPA MRI, EDSS, and CSF‐MBP in relapsing multiple sclerosis patients treated with high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Neurology 1992;42:63‐7. - PubMed
Barnes 1997
-
- Barnes D, Hughes RA, Morris RW, Wade‐Jones O, Brown P, Britton T, et al. Randomised trial of oral and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute relapses in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1997;349(9056):902‐6. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1997097394] - PubMed
Brooks 2013
-
- Brooks M. ACTH pulse therapy may benefit breakthrough MS. American Academy of Neurology (AAN) 65th Annual Meeting; March 16‐23; San Diego, California. 2013; Vol. Abstract P04.269.
Burton 2012
Ciccone 2008
Compston 1999
FDA 2010
-
- Anderson B, ChairDiem‐Kieu H. Peripheral and central nervous system drugs advisory committee UCM215396, 2010. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/advisorycommittees/committeesmeetingmateria... (accessed 31 March 2013).
Gal 2012
Glaser 1951
-
- Glaser GH, Merritt HH. Effect of ACTH and cortisone in multiple sclerosis. Transactions of the American Neurological Association 1951;56:130‐3. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kurtzke 1983
-
- Kurtzke JF. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983;33(11):1444‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levine 2012
Lindquist 2011
-
- Lindquist S, Hassinger S, Lindquist JA, Sailer M. The balance of pro‐inflammatory and trophic factors in multiple sclerosis patients: effects of acute relapse and immunomodulatory treatment. Multiple Sclerosis 2011;17(7):851‐66. - PubMed
Lublin 1996
-
- Lublin FD, Reingold SC. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA). Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 1996;46(4):907‐11. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1996125709] - PubMed
Martinelli 2009
-
- Martinelli V, Rocca MA, Annovazzi P, Pulizzi A, Rodegher M, Martinelli Boneschi F, et al. A short‐term randomized MRI study of high‐dose oral vs intravenous methylprednisolone in MS. Neurology 2009;73(22):1842‐8. - PubMed
Martínez‐Cáceres 2002
-
- Martínez‐Cáceres EM, Barrau MA, Brieva L, Espejo C, Barberà N, Montalban X. Treatment with methylprednisolone in relapses of multiple sclerosis patients: immunological evidence of immediate and short‐term but not long‐lasting effects. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 2002;127(1):165‐71. - PMC - PubMed
McDonald 1977
-
- McDonald WI, Halliday AM. Diagnosis and classification of multiple sclerosis. British Medical Bullettin 1977;33(1):4‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
McEwen 1997
-
- McEwen BS, Biron CA, Brunson KW, Bulloch K, Chambers WH, Dhabhar FS, et al. The role of adrenocorticoids as modulators of immune function in health and disease: neural endocrine and immune interactions. Brain Research. Brain Research Reviews 1997;23(1‐2):79‐133. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1997063673] - PubMed
Meyers 1992
-
- Meyers LW. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with ACTH and corticosteroids. In: Rudick RA, Goodkin DE editor(s). Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Trial Design, Results and Future Perspectives. 1st Edition. London: Springer Verlag, 1992:135‐56.
Morrow 2009
-
- Morrow SA, Metz LM, Kremenchutzky M. High dose oral steroids commonly used to treat relapses in Canadian MS clinics. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 2009;36(2):213‐5. - PubMed
Poser 1983
-
- Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Ebers GC, et al. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Annals of Neurology 1983;13(3):227‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pugliatti 2002
-
- Pugliatti M, Sotgiu S, Rosati G. The worldwide prevalence of multiple sclerosis. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2002;104:182‐91. - PubMed
Rentzos 2008
-
- Rentzos M, Nikolaou C, Rombos A, Evangelopoulos ME, Kararizou E, Koutsis G, et al. Effect of treatment with methylprednisolone on the serum levels of IL‐12, IL‐10 and CCL2 chemokine in patients with multiple sclerosis in relapse. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2008;110(10):992‐6. - PubMed
Repovic 2011
-
- Repovic P, Lublin FD. Treatment of multiple sclerosis exacerbations. Neurologic Clinics 2011;29:369‐400. - PubMed
Review Manager 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2013.
Sapolsky 2000
-
- Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocrine Reviews 2000;21(1):55‐89. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schimmer 2001
-
- Schimmer BP, Parker KL. ACTH, adrenocortical steroids and their synthetic analogs. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE editor(s). Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacologic Basis of Therapeutics. New York: McGraw Hill, 2001:1649‐77.
Sellebierg 2005
-
- Sellebjerg F, Barnes D, Filippini G, Midgard R, Montalban X, Rieckmann P, et al. EFNS guideline on treatment of multiple sclerosis relapses: report of an EFNS task force on treatment of multiple sclerosis relapses. European Journal of Neurology 2005;12:939‐46. - PubMed
Sellebjerg 2003
-
- Sellebjerg F, Jensen CV, Larsson HB, Frederiksen JL. Gadolinium‐enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predicts response to methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 2003;9(1):102‐7. - PubMed
Thompson 1989
-
- Thompson AJ, Kennard C, Swash M, Summers B, Yuill GM, Shepherd DI, et al. Relative efficacy of intravenous methylprednisolone and ACTH in the treatment of acute relapse in MS. Neurology 1989;39(7):969‐71. [MEDLINE: ; EMBASE‐1989170466] - PubMed
Tremlett 1998
WHO 2008
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) and Multiple Sclerosis International Federation. Atlas: Multiple Sclerosis Resources in the World 2008. http://www.who.int/mental_health/neurology/Atlas_MS_WEB.pdf (accessed 31 March 2013). [ISBN 978 92 4 156375 8]
Willer 2000
-
- Willer CJ, Ebers GC. Susceptibility to multiple sclerosis: interplay between genes and environment. Current Opinion in Neurology 2000;13(3):241‐7. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

