Characterization of the catalytic domain of Clostridium novyi alpha-toxin
- PMID: 11035748
- PMCID: PMC97722
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.11.6378-6383.2000
Characterization of the catalytic domain of Clostridium novyi alpha-toxin
Abstract
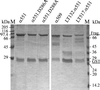
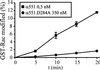
Clostridium novyi alpha-toxin belongs to the family of large clostridial cytotoxins which act on cells through the modification of small GTP-binding proteins. We present here an analysis of the catalytic domain of alpha-toxin. A NH(2)-terminal 551-amino-acid fragment, alpha 551, was found to contain the full enzyme activity of the holotoxin, whereas a slightly shortened fragment encompassing 509 amino acids showed no detectable enzyme activity. Further characterization of the enzymatically active fragment alpha 551 revealed a substrate specificity for both UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and UDP-glucose. A Michaelis-Menten constant of 17 microM was determined for the substrate UDP-N-acetylglucosamine, while that for UDP-glucose was about 20 times higher, indicating a weaker affinity of the toxin for the latter substrate. Mutation of the aspartic acids of a conserved motif DXD within alpha 551 reduced enzyme activity >700-fold and inhibited cytotoxicity after microinjection in cells. Inhibition of enzyme activity of the DXD mutant could be partially overcome by increased concentrations of manganese ions, suggesting the involvement of these aspartic acids in Mn(2+) binding. By construction of chimeras of enzymatically active fragments of C. sordellii lethal toxin and C. novyi alpha-toxin, we located the region involved in nucleotide-sugar specificity to amino acids 133 through 517.
Figures





References
-
- Bette P, Oksche A, Mauler F, von Eichel-Streiber C, Popoff M R, Habermann E. A comparative biochemical, pharmacological and immunological study of Clostridium novyi α-toxin, C. difficile toxin B, and C. sordellii lethal toxin. Toxicon. 1991;29:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Busch C, Hofmann F, Gerhard R, Aktories K. Involvement of a conserved tryptophan residue in the UDP-glucose binding of large clostridial cytotoxin glycosyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:13228–13234. - PubMed
-
- Busch C, Hofmann F, Selzer J, Munro J, Jeckel D, Aktories K. A common motif of eukaryotic glycosyltransferases is essential for the enzyme activity of large clostridial cytotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19566–19572. - PubMed
-
- Charnock S J, Davies G J. Structure of the nucleotide-diphospho-sugar transferase, SpsA from Bacillus subtilis, in native and nucleotide-complexed forms. Biochemistry. 1999;38:6380–6385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

