Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A
- PMID: 11035810
- PMCID: PMC17277
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.220413597
Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A
Abstract
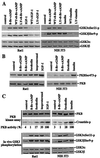
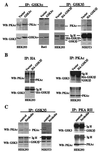
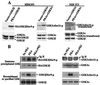
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is implicated in multiple biological processes including metabolism, gene expression, cell fate determination, proliferation, and survival. GSK-3 activity is inhibited through phosphorylation of serine 21 in GSK-3 alpha and serine 9 in GSK-3 beta. These serine residues of GSK-3 have been previously identified as targets of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a serine/threonine kinase located downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Here, we show that serine 21 in GSK-3 alpha and serine 9 in GSK-3 beta are also physiological substrates of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. Protein kinase A physically associates with, phosphorylates, and inactivates both isoforms of GSK-3. The results indicate that depending on the stimulatory context, the activity of GSK-3 can be modulated either by growth factors that work through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B cascade or by hormonal stimulation of G protein-coupled receptors that link to changes in intracellular cAMP levels.
Figures

References
-
- Plyte S E, Hughes K, Nikolakaki E, Pulverer B J, Woodgett J R. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1992:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Welsh G L, Welson C, Proud C G. Trends Cell Biol. 1996;6:274–279. - PubMed
-
- Harwood A J, Plyte S E, Woodgett J R, Strutt H, Kay R R. Cell. 1995;80:139–148. - PubMed
-
- Siegfried E, Chou T B, Perrimon N. Cell. 1992;71:1167–1179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

