Once-daily dosing in dogs optimizes daptomycin safety
- PMID: 11036005
- PMCID: PMC101585
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.2948-2953.2000
Once-daily dosing in dogs optimizes daptomycin safety
Abstract
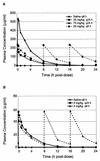
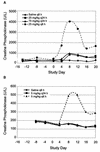
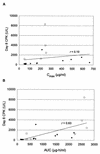
Daptomycin is a novel lipopeptide antibiotic with potent bactericidal activity against most clinically important gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains. Daptomycin has been shown to have an effect on skeletal muscle. To guide the clinical dosing regimen with the potential for the least effect on skeletal muscle, two studies were conducted with dogs to compare the effects of repeated intravenous administration every 24 h versus every 8 h for 20 days. The data suggest that skeletal-muscle effects were more closely related to the dosing interval than to either the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma or the area under the concentration-time curve. Both increases in serum creatine phosphokinase activity and the incidence of myopathy observed at 25 mg/kg of body weight every 8 h were greater than those observed at 75 mg/kg every 24 h despite the lower maximum concentration of drug in plasma. Similarly, the effects observed at 25 mg/kg every 8 h were greater than those observed at 75 mg/kg every 24 h at approximately the same area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h. Once-daily administration appeared to minimize the potential for daptomycin-related skeletal-muscle effects, possibly by allowing for more time between doses for repair of subclinical effects. Thus, these studies with dogs suggest that once-daily dosing of daptomycin in humans should have the potential to minimize skeletal-muscle effects. In fact, interim results of ongoing clinical trials, which have focused on once-daily dosing, appear to be consistent with this conclusion.
Figures

References
-
- Clarkson P, Nosaka K, Braun B. Muscle function after exercise-induced muscle damage and rapid adaptation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992;24:512–520. - PubMed
-
- Hanberger H, Nilsson L E, Maller R, Isaksson B. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin and vancomycin on Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated by studies of initial killing and postantibiotic effect and influence of Ca2+ and albumin on these drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:1710–1716. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

