Genetic analysis of azole resistance in the Darlington strain of Candida albicans
- PMID: 11036010
- PMCID: PMC101590
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.2985-2990.2000
Genetic analysis of azole resistance in the Darlington strain of Candida albicans
Abstract
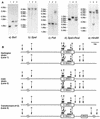
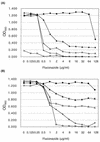
High-level azole resistance in the Darlington strain of Candida albicans was investigated by gene replacement in C. albicans and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We sequenced the ERG11 gene, which encodes the sterol C(14)alpha-demethylase, from our copy of the Darlington strain. Both alleles contained the histidine for tyrosine substitution at position 132 (Y132H) reported in Darlington by others, but we also found a threonine-for-isoleucine substitution (I471T) not previously reported in the C. albicans ERG11. The encoded I471T change in amino acids conferred azole resistance when overexpressed alone and increased azole resistance when added to the Y132H amino acid sequence in an S. cerevisiae expression system. Replacement of one copy of ERG11 in an azole-susceptible strain of C. albicans with a single copy of the Darlington ERG11 resulted in expression of the integrated copy and a modest increase in azole resistance. The profound azole resistance of the Darlington strain is the result of multiple mutations.
Figures

References
-
- Favre B, Didmon M, Ryder N S. Multiple amino acid substitutions in lanosterol 14α-demethylase contribute to azole resistance in Candida albicans. Microbiology. 1999;145:2715–2725. - PubMed
-
- Fujimura H, Sakura Y. Simplified isolation of chromosomal and plasmid DNA from yeast. BioTechniques. 1993;14:538–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

