Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced death by fluoroquinolones
- PMID: 11036044
- PMCID: PMC101624
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.11.3169-3173.2000
Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced death by fluoroquinolones
Abstract
Because fluoroquinolones have an immunomodulatory effect on cytokine production by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated human monocytes, we examined the effect of fluoroquinolones on the survival of mice injected with a lethal dose of LPS. Trovafloxacin (100 mg/kg), ciprofloxacin (250 mg/kg), and tosufloxacin (100 mg/kg) protected 75% (P = 0.0001), 25% (P = 0.002), and 50% (P = 0.002), respectively, of mice against death. The fluoroquinolones significantly reduced serum levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in LPS-treated mice. The protective effects of fluoroquinolones in LPS-induced shock in mice may also occur in humans.
Figures
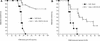

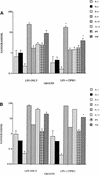
References
-
- Abraham E, Anzueto A, Gutierrez G, Tessler S, Pedro G S, Wunderink R, Nogare A D, Nasraway S, Berman S, Cooney R, Levy H, Baughman R, Rumbark M, Light R B, Poole L, Allred R, Constant J, Pennington J, Porter S the Norasept II Study Group. Double-blind randomised controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumour necrosis factor in treatment of septic shock. Lancet. 1998;351:929–933. - PubMed
-
- Anderson B O, Bensard D D, Harken A H. The role of platelet activating factor and its antagonists in shock, gram negative sepsis and multiple organ failure Surg. Gynecol Obstet. 1991;172:415–424. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Bone R C, Balk R A, Fein A M, Perl T M, Wenzel R P, Reines H D, Quenzer R W, Iberti T J, Macintyre N, Schein R M. A second large controlled clinical study of E5, a monoclonal antibody to endotoxin: results of a prospective, multicenter, randomized, clinical trial. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:994–1006. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

