Ectodomain shedding of epidermal growth factor receptor ligands is required for keratinocyte migration in cutaneous wound healing
- PMID: 11038170
- PMCID: PMC2192647
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.2.209
Ectodomain shedding of epidermal growth factor receptor ligands is required for keratinocyte migration in cutaneous wound healing
Abstract
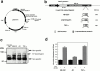
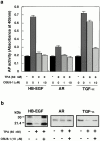
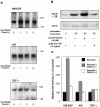
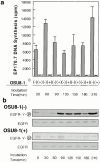
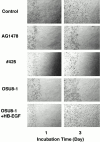
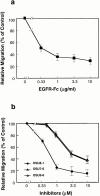
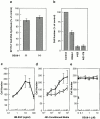
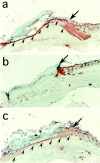
Keratinocyte proliferation and migration are essential to cutaneous wound healing and are, in part, mediated in an autocrine fashion by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-ligand interactions. EGFR ligands are initially synthesized as membrane-anchored forms, but can be processed and shed as soluble forms. We provide evidence here that wound stimuli induce keratinocyte shedding of EGFR ligands in vitro, particularly the ligand heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF). The resulting soluble ligands stimulated transient activation of EGFR. OSU8-1, an inhibitor of EGFR ligand shedding, abrogated the wound-induced activation of EGFR and caused suppression of keratinocyte migration in vitro. Soluble EGFR-immunoglobulin G-Fcgamma fusion protein, which is able to neutralize all EGFR ligands, also suppressed keratinocyte migration in vitro. The application of OSU8-1 to wound sites in mice greatly retarded reepithelialization as the result of a failure in keratinocyte migration, but this effect could be overcome if recombinant soluble HB-EGF was added along with OSU8-1. These findings indicate that the shedding of EGFR ligands represents a critical event in keratinocyte migration, and suggest their possible use as an effective clinical treatment in the early phases of wound healing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel function of angiotensin II in skin wound healing. Induction of fibroblast and keratinocyte migration by angiotensin II via heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor-mediated EGF receptor transactivation.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 12;281(19):13209-13216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509771200. Epub 2006 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16543233
-
Wound-induced HB-EGF ectodomain shedding and EGFR activation in corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004 Mar;45(3):813-20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.03-0851. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004. PMID: 14985295 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid promoting corneal epithelial wound healing by transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Feb;48(2):636-43. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0203. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17251460 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-anchored growth factors, the epidermal growth factor family: beyond receptor ligands.Cancer Sci. 2008 Feb;99(2):214-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00676.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18271917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAM-mediated ectodomain shedding of HB-EGF in receptor cross-talk.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Aug 1;1751(1):110-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.11.009. Epub 2004 Dec 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16054021 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual modes of motility at the leading edge of migrating epithelial cell sheets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 25;109(39):15799-804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210992109. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23019364 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial range of autocrine signaling: modeling and computational analysis.Biophys J. 2001 Oct;81(4):1854-67. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75837-7. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11566760 Free PMC article.
-
Free edges in epithelia as cues for motility.Cell Adh Migr. 2011 Mar-Apr;5(2):106-10. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.2.13728. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 20953155 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear IL-33 Plays an Important Role in EGFR-Mediated Keratinocyte Migration by Regulating the Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 and NF-κB.JID Innov. 2023 Apr 28;3(4):100205. doi: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2023.100205. eCollection 2023 Jul. JID Innov. 2023. PMID: 37441125 Free PMC article.
-
SRC-family tyrosine kinases in wound- and ligand-induced epidermal growth factor receptor activation in human corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Jul;47(7):2832-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1361. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16799022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black R.A., Rauch C.T., Kozlosky C.J., Peschon J.J., Slack J.L., Wolfson M.F., Castner B.J., Stocking K.L., Reddy P., Srinivasan S. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumor-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature. 1997;385:729–733. - PubMed
-
- Blotnick S., Peoples G.E., Freeman M.R., Eberlein T.J., Klagsbrun M. T lymphocytes synthesize and export heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor, mitogens for vascular cells and fibroblastsdifferential production and release by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:2890–2894. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brachmann R., Lindquist P.B., Nagashima M., Kohr W., Lipari T., Napier M., Derynck R. Transmembrane TGF-α precursors activate EGF/TGF-α receptors. Cell. 1989;56:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Chen C.A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfera highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988;6:632–638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

