Indications for a novel muscular dystrophy pathway. gamma-filamin, the muscle-specific filamin isoform, interacts with myotilin
- PMID: 11038172
- PMCID: PMC2192634
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.2.235
Indications for a novel muscular dystrophy pathway. gamma-filamin, the muscle-specific filamin isoform, interacts with myotilin
Abstract
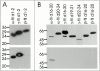
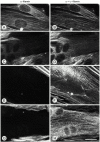
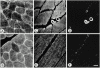
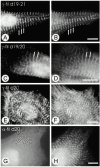
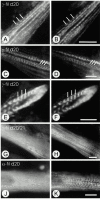
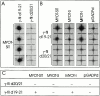
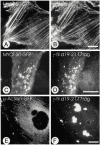
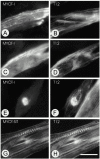
gamma-Filamin, also called ABP-L, is a filamin isoform that is specifically expressed in striated muscles, where it is predominantly localized in myofibrillar Z-discs. A minor fraction of the protein shows subsarcolemmal localization. Although gamma-filamin has the same overall structure as the two other known isoforms, it is the only isoform that carries a unique insertion in its immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain 20. Sequencing of the genomic region encoding this part of the molecule shows that this insert is encoded by an extra exon. Transient transfections of the insert-bearing domain in skeletal muscle cells and cardiomyocytes show that this single domain is sufficient for targeting to developing and mature Z-discs. The yeast two-hybrid method was used to identify possible binding partners for the insert-bearing Ig-like domain 20 of gamma-filamin. The two Ig-like domains of the recently described alpha-actinin-binding Z-disc protein myotilin were found to interact directly with this filamin domain, indicating that the amino-terminal end of gamma-filamin may be indirectly anchored to alpha-actinin in the Z-disc via myotilin. Since defects in the myotilin gene were recently reported to cause a form of autosomal dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, our findings provide a further contribution to the molecular understanding of this disease.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Z-disc proteins myotilin and FATZ-1 interact with each other and are connected to the sarcolemma via muscle-specific filamins.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3739-49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02484. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16076904
-
Expression of distinct classes of titin isoforms in striated and smooth muscles by alternative splicing, and their conserved interaction with filamins.J Mol Biol. 2006 Sep 29;362(4):664-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.077. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16949617
-
New N-RAP-binding partners alpha-actinin, filamin and Krp1 detected by yeast two-hybrid screening: implications for myofibril assembly.J Cell Sci. 2003 Jun 1;116(Pt 11):2169-78. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00425. Epub 2003 Apr 8. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12692149
-
Telethonin and other new proteins of the Z-disc of skeletal muscle.IUBMB Life. 2001 May;51(5):275-82. doi: 10.1080/152165401317190761. IUBMB Life. 2001. PMID: 11699871 Review.
-
The palladin/myotilin/myopalladin family of actin-associated scaffolds.Int Rev Cytol. 2005;246:31-58. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(05)46002-7. Int Rev Cytol. 2005. PMID: 16164966 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Insight into the Role of Calpains in Post-mortem Meat Tenderization in Domestic Animals: A review.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013 Mar;26(3):443-54. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12365. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 25049808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FLNC-Associated Myofibrillar Myopathy: New Clinical, Functional, and Proteomic Data.Neurol Genet. 2021 May 18;7(3):e590. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000590. eCollection 2021 Jun. Neurol Genet. 2021. PMID: 34235269 Free PMC article.
-
Myotilin dynamics in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011 Dec;68(12):661-70. doi: 10.1002/cm.20542. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 22021208 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygous expression of the myofibrillar myopathy-associated p.W2710X filamin C variant reveals major pathomechanisms of sarcomeric lesion formation.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Sep 4;8(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01001-9. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32887649 Free PMC article.
-
Filamin A, the Arp2/3 complex, and the morphology and function of cortical actin filaments in human melanoma cells.J Cell Biol. 2001 Nov 12;155(4):511-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105148. Epub 2001 Nov 12. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11706047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-el-Basset E.M., Ahmed I., Fedoroff S. Actin and actin-binding proteins in differentiating astroglia in tissue culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 1991;30:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Ayscough K.R. In vivo functions of actin-binding proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998;10:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Barry C.P., Xie J., Lemmon V., Young A.P. Molecular characterization of a multipromoter gene encoding a chicken filamin protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:25577–25586. - PubMed
-
- Bröcker F., Bardenheuer W., Vieten L., Jülicher K., Werner N., Marguitan G., Michael D., Opalka B., Schütte J. Assignment of human filamin gene FLNB to human chromosome band 3p14.3 and identification of YACs containing the complete FLNB transcribed region. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1999;85:267–268. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

