The dynamin-related GTPase, Mgm1p, is an intermembrane space protein required for maintenance of fusion competent mitochondria
- PMID: 11038181
- PMCID: PMC2192650
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.2.341
The dynamin-related GTPase, Mgm1p, is an intermembrane space protein required for maintenance of fusion competent mitochondria
Abstract
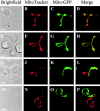
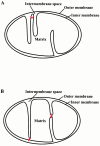
Mutations in the dynamin-related GTPase, Mgm1p, have been shown to cause mitochondrial aggregation and mitochondrial DNA loss in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, but Mgm1p's exact role in mitochondrial maintenance is unclear. To study the primary function of MGM1, we characterized new temperature sensitive MGM1 alleles. Examination of mitochondrial morphology in mgm1 cells indicates that fragmentation of mitochondrial reticuli is the primary phenotype associated with loss of MGM1 function, with secondary aggregation of mitochondrial fragments. This mgm1 phenotype is identical to that observed in cells with a conditional mutation in FZO1, which encodes a transmembrane GTPase required for mitochondrial fusion, raising the possibility that Mgm1p is also required for fusion. Consistent with this idea, mitochondrial fusion is blocked in mgm1 cells during mating, and deletion of DNM1, which encodes a dynamin-related GTPase required for mitochondrial fission, blocks mitochondrial fragmentation in mgm1 cells. However, in contrast to fzo1 cells, deletion of DNM1 in mgm1 cells restores mitochondrial fusion during mating. This last observation indicates that despite the phenotypic similarities observed between mgm1 and fzo1 cells, MGM1 does not play a direct role in mitochondrial fusion. Although Mgm1p was recently reported to localize to the mitochondrial outer membrane, our studies indicate that Mgm1p is localized to the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Based on our localization data and Mgm1p's structural homology to dynamin, we postulate that it functions in inner membrane remodeling events. In this context, the observed mgm1 phenotypes suggest that inner and outer membrane fission is coupled and that loss of MGM1 function may stimulate Dnm1p-dependent outer membrane fission, resulting in the formation of mitochondrial fragments that are structurally incompetent for fusion.
Figures


Comment in
-
A mitochondrial division apparatus takes shape.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 16;151(2):F1-4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.2.f1. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11038192 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Beech P.L., Nheu T., Schultz T., Herbert S., Lithgow T., Gilson P.R., McFadden G.I. Mitochondrial FtsZ in a chromophyte alga. Science. 2000;287:1276–1279. - PubMed
-
- Glick B.S., Brandt A., Cunningham K., Mueller S., Hallberg R.L., Schatz G. Cytochromes c1 and b2 are sorted to the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria by a stop-transfer mechanism. Cell. 1992;69:809–822. - PubMed
-
- Guan K., Farh L., Marshall T.K., Deschenes R.J. Normal mitochondrial structure and genome maintenance in yeast requires the dynamin-like product of the MGM1 gene. Curr. Genetics. 1993;24:141–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

