Raf induces TGFbeta production while blocking its apoptotic but not invasive responses: a mechanism leading to increased malignancy in epithelial cells
- PMID: 11040215
- PMCID: PMC316988
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.181700
Raf induces TGFbeta production while blocking its apoptotic but not invasive responses: a mechanism leading to increased malignancy in epithelial cells
Abstract
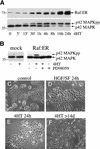
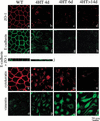
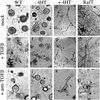
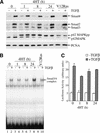
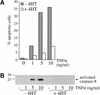
c-Raf-1 is a major effector of Ras proteins, responsible for activation of the ERK MAP kinase pathway and a critical regulator of both normal growth and oncogenic transformation. Using an inducible form of Raf in MDCK cells, we have shown that sustained activation of Raf alone is able to induce the transition from an epithelial to a mesenchymal phenotype. Raf promoted invasive growth in collagen gels, a characteristic of malignant cells; this was dependent on the operation of an autocrine loop involving TGFbeta, whose secretion was induced by Raf. TGFbeta induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in normal MDCK cells: Activation of Raf led to inhibition of the ability of TGFbeta to induce apoptosis but not growth retardation. ERK has been reported previously to inhibit TGFbeta signaling via phosphorylation of the linker region of Smads, which prevents their translocation to the nucleus. However, we found no evidence in this system that ERK can significantly influence the function of Smad2, Smad3, and Smad4 at the level of nuclear translocation, DNA binding, or transcriptional activation. Instead, strong activation of Raf caused a broad protection of these cells from various apoptotic stimuli, allowing them to respond to TGFbeta with increased invasiveness while avoiding cell death. The Raf-MAP kinase pathway thus synergizes with TGFbeta in promoting malignancy but does not directly impair TGFbeta-induced Smad signaling.
Figures

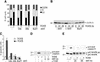
Similar articles
-
A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/ Smad signaling by oncogenic Ras.Genes Dev. 1999 Apr 1;13(7):804-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.7.804. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10197981 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ras and Mapks in TGFbeta signaling.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Mar-Jun;11(1-2):23-35. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00026-x. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10708950 Review.
-
Ras and TGF[beta] cooperatively regulate epithelial cell plasticity and metastasis: dissection of Ras signaling pathways.J Cell Biol. 2002 Jan 21;156(2):299-313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109037. Epub 2002 Jan 14. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11790801 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of Ras/MAPK pathway activation by transforming growth factor beta for transforming growth factor beta 1 production in a Smad-dependent pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):30765-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000039200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10843986
-
Resistance to transforming growth factor β-mediated tumor suppression in melanoma: are multiple mechanisms in place?Carcinogenesis. 2010 Oct;31(10):1710-7. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq155. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20656791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beta3 integrin and Src facilitate transforming growth factor-beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8(4):R42. doi: 10.1186/bcr1524. Breast Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16859511 Free PMC article.
-
TGFβ-induced changes in membrane curvature influence Ras oncoprotein membrane localization.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 5;12(1):13486. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17482-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35931724 Free PMC article.
-
Smad phosphoisoform signals in acute and chronic liver injury: similarities and differences between epithelial and mesenchymal cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jan;347(1):225-43. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1178-6. Epub 2011 May 31. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 21626291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An autocrine TGF-beta/ZEB/miR-200 signaling network regulates establishment and maintenance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 May 15;22(10):1686-98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0103. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21411626 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways.Cell Res. 2009 Jan;19(1):71-88. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.302. Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19002158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhurst RJ, Balmain A. Genetic events and the role of TGFβ in epithelial tumor progression. J Pathol. 1999;187:82–90. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier W, Weidner KM, Behrens J. Molecular mechanisms leading to loss of differentiation and gain of invasiveness in epithelial cells. J Cell Sci (Suppl.) 1993;17:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C, Meyer D, Riethmacher D. Factors controlling growth, motility, and morphogenesis of normal and malignant epithelial cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1995;160:221–266. - PubMed
-
- Bosch E, Cherwinski H, Peterson D, McMahon M. Mutations of critical amino acids affect the biological and biochemical properties of oncogenic A-Raf and Raf-1. Oncogene. 1997;15:1021–1033. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
