Spt5 and spt6 are associated with active transcription and have characteristics of general elongation factors in D. melanogaster
- PMID: 11040216
- PMCID: PMC316994
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.831900
Spt5 and spt6 are associated with active transcription and have characteristics of general elongation factors in D. melanogaster
Abstract
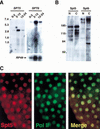
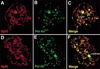
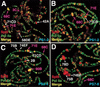
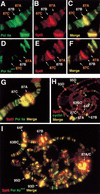
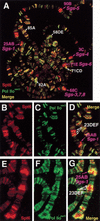
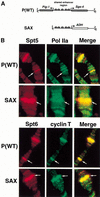
The Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 proteins are conserved throughout eukaryotes and are believed to play critical and related roles in transcription. They have a positive role in transcription elongation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in the activation of transcription by the HIV Tat protein in human cells. In contrast, a complex of Spt4 and Spt5 is required in vitro for the inhibition of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) elongation by the drug DRB, suggesting also a negative role in vivo. To learn more about the function of the Spt4/Spt5 complex and Spt6 in vivo, we have identified Drosophila homologs of Spt5 and Spt6 and characterized their localization on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. We find that Spt5 and Spt6 localize extensively with the phosphorylated, actively elongating form of Pol II, to transcriptionally active sites during salivary gland development and upon heat shock. Furthermore, Spt5 and Spt6 do not colocalize widely with the unphosphorylated, nonelongating form of Pol II. These results strongly suggest that Spt5 and Spt6 play closely related roles associated with active transcription in vivo.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-resolution localization of Drosophila Spt5 and Spt6 at heat shock genes in vivo: roles in promoter proximal pausing and transcription elongation.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2635-49. doi: 10.1101/gad.844200. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040217 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 control transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes Dev. 1998 Feb 1;12(3):357-69. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.3.357. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9450930 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila ELL is associated with actively elongating RNA polymerase II on transcriptionally active sites in vivo.EMBO J. 2001 Nov 1;20(21):6104-14. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6104. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11689450 Free PMC article.
-
The pleiotropic roles of SPT5 in transcription.Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):53-69. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2103366. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 35876486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Spt4-Spt5 complex: a multi-faceted regulator of transcription elongation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):105-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Presenilin-based genetic screens in Drosophila melanogaster identify novel notch pathway modifiers.Genetics. 2006 Apr;172(4):2309-24. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.035170. Epub 2006 Jan 16. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16415372 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of P-TEFb by the MEK1-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway contributes to stimulated transcription elongation of immediate early genes in neuroendocrine cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(5):1630-43. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01767-07. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18086894 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila dosage compensation complex binds to polytene chromosomes independently of developmental changes in transcription.Genetics. 2006 Feb;172(2):963-74. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.045286. Epub 2005 Aug 3. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16079233 Free PMC article.
-
The transcript elongation factor SPT4/SPT5 is involved in auxin-related gene expression in Arabidopsis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4332-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku096. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24497194 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast genetic analysis reveals the involvement of chromatin reassembly factors in repressing HIV-1 basal transcription.PLoS Genet. 2009 Jan;5(1):e1000339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000339. Epub 2009 Jan 16. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19148280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Archambault J, Pan G, Dahmus GK, Cartier M, Marshall N, Zhang S, Dahmus ME, Greenblatt J. FCP1, the RAP74-interacting subunit of a human protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase IIO. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:27593–27601. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. I. Autosomal puffing patterns in a laboratory stock of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1967;21:398–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
