High-resolution localization of Drosophila Spt5 and Spt6 at heat shock genes in vivo: roles in promoter proximal pausing and transcription elongation
- PMID: 11040217
- PMCID: PMC316984
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.844200
High-resolution localization of Drosophila Spt5 and Spt6 at heat shock genes in vivo: roles in promoter proximal pausing and transcription elongation
Abstract
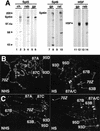
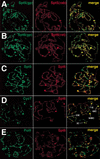
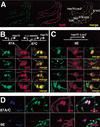
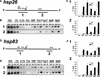
Recent studies have demonstrated roles for Spt4, Spt5, and Spt6 in the regulation of transcriptional elongation in both yeast and humans. Here, we show that Drosophila Spt5 and Spt6 colocalize at a large number of transcriptionally active chromosomal sites on polytene chromosomes and are rapidly recruited to endogenous and transgenic heat shock loci upon heat shock. Costaining with antibodies to Spt6 and to either the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II or cyclin T, a subunit of the elongation factor P-TEFb, reveals that all three factors have a similar distribution at sites of active transcription. Crosslinking and immunoprecipitation experiments show that Spt5 is present at uninduced heat shock gene promoters, and that upon heat shock, Spt5 and Spt6 associate with the 5' and 3' ends of heat shock genes. Spt6 is recruited within 2 minutes of a heat shock, similar to heat shock factor (HSF); moreover, this recruitment is dependent on HSF. These findings provide support for the roles of Spt5 in promoter-associated pausing and of Spt5 and Spt6 in transcriptional elongation in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Bortvin A, Winston F. Evidence that Spt6p controls chromatin structure by a direct interaction with histones. Science. 1996;272:1473–1476. - PubMed
-
- Dahmus ME. The role of multisite phosphorylation in the regulation of RNA polymerase II activity. Prog Nucleic Acid Res and Mol Biol. 1994;48:143–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
