The alpha subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase activates RNA binding by NusA
- PMID: 11040219
- PMCID: PMC316996
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.822900
The alpha subunit of E. coli RNA polymerase activates RNA binding by NusA
Abstract
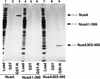
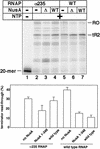
The Escherichia coli NusA protein modulates pausing, termination, and antitermination by associating with the transcribing RNA polymerase core enzyme. NusA can be covalently cross-linked to nascent RNA within a transcription complex, but does not bind RNA on its own. We have found that deletion of the 79 carboxy-terminal amino acids of the 495-amino-acid NusA protein allows NusA to bind RNA in gel mobility shift assays. The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase, as well as the bacteriophage lambda N gene antiterminator protein, bind to carboxy-terminal regions of NusA and enable full-length NusA to bind RNA. Binding of NusA to RNA in the presence of alpha or N involves an amino-terminal S1 homology region that is otherwise inactive in full-length NusA. The interaction of the alpha-CTD with full-length NusA stimulates termination. N may prevent termination by inducing NusA to interact with N utilization (nut) site RNA rather than RNA near the 3' end of the nascent transcript. Sequence analysis showed that the alpha-CTD contains a modified helix-hairpin-helix motif (HhH), which is also conserved in the carboxy-terminal regions of some eubacterial NusA proteins. These HhH motifs may mediate protein-protein interactions in NusA and the alpha-CTD.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Functional importance of regions in Escherichia coli elongation factor NusA that interact with RNA polymerase, the bacteriophage lambda N protein and RNA.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Nov;34(3):523-37. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01618.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10564494
-
Interactions of an Arg-rich region of transcription elongation protein NusA with NUT RNA: implications for the order of assembly of the lambda N antitermination complex in vivo.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 29;310(1):33-49. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4722. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11419935
-
Role of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit in modulation of pausing, termination and anti-termination by the transcription elongation factor NusA.EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):150-61. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8598198 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between RNA polymerase and the elongation factor NusA.RNA Biol. 2010 May-Jun;7(3):272-5. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.3.12021. Epub 2010 May 7. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 20458190 Review.
-
Factor-stimulated intrinsic termination: getting by with a little help from some friends.Transcription. 2022 Aug-Oct;13(4-5):96-108. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2127602. Epub 2022 Sep 25. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 36154805 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nascent RNA length dictates opposing effects of NusA on antitermination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 20;44(11):5378-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw198. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27025650 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-specific 1H, 13C, 15N resonance assignments and secondary structure of the carboxyterminal domain of the E. coli transcription factor NusA.J Biomol NMR. 2004 Feb;28(2):193-4. doi: 10.1023/B:JNMR.0000013819.55179.13. J Biomol NMR. 2004. PMID: 14755165 No abstract available.
-
Crystal structures of transcription factor NusG in light of its nucleic acid- and protein-binding activities.EMBO J. 2002 Sep 2;21(17):4641-53. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf455. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12198166 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Transcript Elongation.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015;69:49-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091014-104047. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26132790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SuhB is an integral part of the ribosomal antitermination complex and interacts with NusA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6504-6518. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz442. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31127279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blatter EE, Ross W, Tang H, Gourse RL, Ebright RH. Domain organization of RNA polymerase α subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994;78:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Burgess RR, Jendrisak JJ. A procedure for the rapid, large-scale purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975;14:4634–4638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
