Role of hippocampal signaling pathways in long-term memory formation of a nonassociative learning task in the rat
- PMID: 11040265
- PMCID: PMC311352
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.34600
Role of hippocampal signaling pathways in long-term memory formation of a nonassociative learning task in the rat
Abstract
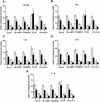
Long-term habituation to a novel environment is one of the most elementary forms of nonassociative learning. Here we studied the effect of pre- or posttraining intrahippocampal administration of drugs acting on specific molecular targets on the retention of habituation to a 5-min exposure to an open field measured 24 h later. We also determined whether the exposure to a novel environment resulted in the activation of the same intracellular signaling cascades previously shown to be activated during hippocampal-dependent associative learning. The immediate posttraining bilateral infusion of CNQX (1 microg/side), an AMPA/kainate glutamate receptor antagonist, or of muscimol (0.03 microg/side), a GABA(A) receptor agonist, into the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus impaired long-term memory of habituation. The NMDA receptor antagonist AP5 (5 microg/side) impaired habituation when infused 15 min before, but not when infused immediately after, the 5-min training session. In addition, KN-62 (3.6 ng/side), an inhibitor of calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), was amnesic when infused 15 min before or immediately and 3 h after training. In contrast, the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) inhibitor Rp-cAMPS, the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MAPKK) inhibitor PD098059, and the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin, at doses that fully block memory formation of inhibitory avoidance learning, did not affect habituation to a novel environment. The detection of spatial novelty is associated with a sequential activation of PKA, ERKs (p44 and p42 MAPKs) and CaMKII and the phosphorylation of c-AMP responsive element-binding protein (CREB) in the hippocampus. These findings suggest that memory formation of spatial habituation depends on the functional integrity of NMDA and AMPA/kainate receptors and CaMKII activity in the CA1 region of the hippocampus and that the detection of spatial novelty is accompanied by the activation of at least three different hippocampal protein kinase signaling cascades.
Figures
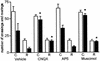
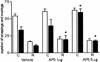

Similar articles
-
Different hippocampal molecular requirements for short- and long-term retrieval of one-trial avoidance learning.Behav Brain Res. 2000 Jun 15;111(1-2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(00)00137-6. Behav Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10840135
-
Memory consolidation induces N-methyl-D-aspartic acid-receptor- and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-dependent modifications in alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor properties.Neuroscience. 2005;136(2):397-403. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.08.007. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16182449
-
Novelty causes time-dependent retrograde amnesia for one-trial avoidance in rats through NMDA receptor- and CaMKII-dependent mechanisms in the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Sep;11(9):3323-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00742.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10510197
-
CaM kinase II in long-term potentiation.Neurochem Int. 1996 Apr;28(4):343-58. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(95)00097-6. Neurochem Int. 1996. PMID: 8740440 Review.
-
Role of the amygdala, hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in memory consolidation and expression.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1993 Jun;26(6):573-89. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1993. PMID: 7504967 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between Experimental Bacterial Meningitis and Periapical Lesion.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 May;9(5):DF01-3. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/8477.5986. Epub 2015 May 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26155479 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral tagging of extinction learning.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jan 15;110(3):1071-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220875110. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23277583 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction restores carbon ion-induced cognitive deficits via co-activation of NRF2 and PINK1 signaling pathway.Redox Biol. 2018 Jul;17:143-157. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.04.012. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29689442 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Proteins Influence Novelty-Seeking Behavior and Alter Region-Specific Transcriptional Responses to Chronic Nicotine Treatment in HIV-1Tg Rats.Nicotine Tob Res. 2017 Sep 1;19(9):1024-1032. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntx047. Nicotine Tob Res. 2017. PMID: 28339662 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal calpain is required for the consolidation and reconsolidation but not extinction of contextual fear memory.Mol Brain. 2017 Dec 19;10(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13041-017-0341-8. Mol Brain. 2017. PMID: 29258546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nature Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bernabeu R, Bevilaqua L, Ardenghi P, Bromberg E, Schmitz P, Bianchin M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. Involvement of hippocampal cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathways in a late memory consolidation phase of aversively motivated learning in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94:7041–7046. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
