AHM1, a novel type of nuclear matrix-localized, MAR binding protein with a single AT hook and a J domain-homologous region
- PMID: 11041885
- PMCID: PMC149128
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.10.1903
AHM1, a novel type of nuclear matrix-localized, MAR binding protein with a single AT hook and a J domain-homologous region
Abstract
Interactions between the nuclear matrix and special regions of chromosomal DNA called matrix attachment regions (MARs) have been implicated in various nuclear functions. We have identified a novel protein from wheat, AT hook-containing MAR binding protein1 (AHM1), that binds preferentially to MARs. A multidomain protein, AHM1 has the special combination of a J domain-homologous region and a Zn finger-like motif (a J-Z array) and an AT hook. For MAR binding, the AT hook at the C terminus was essential, and an internal portion containing the Zn finger-like motif was additionally required in vivo. AHM1 was found in the nuclear matrix fraction and was localized in the nucleoplasm. AHM1 fused to green fluorescent protein had a speckled distribution pattern inside the nucleus. AHM1 is most likely a nuclear matrix component that functions between intranuclear framework and MARs. J-Z arrays can be found in a group of (hypothetical) proteins in plants, which may share some functions, presumably to recruit specific Hsp70 partners as co-chaperones.
Figures

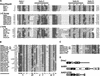
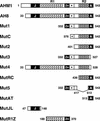




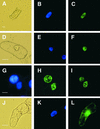
References
-
- Berezney, R., and Jeon, K.W. (1995). Nuclear Matrix. Structural and Functional Organization. (San Diego, CA: Academic Press).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

