Viral vascular endothelial growth factor plays a critical role in orf virus infection
- PMID: 11044114
- PMCID: PMC110944
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10699-10706.2000
Viral vascular endothelial growth factor plays a critical role in orf virus infection
Abstract
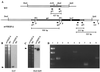
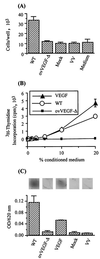
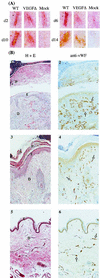
Infection by the parapoxvirus orf virus causes proliferative skin lesions in which extensive capillary proliferation and dilation are prominent histological features. This infective phenotype may be linked to a unique virus-encoded factor, a distinctive new member of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family of molecules. We constructed a recombinant orf virus in which the VEGF-like gene was disrupted and show that inactivation of this gene resulted in the loss of three VEGF activities expressed by the parent virus: mitogenesis of vascular endothelial cells, induction of vascular permeability, and activation of VEGF receptor 2. We used the recombinant orf virus to assess the contribution of the viral VEGF to the vascular response seen during orf virus infection of skin. Our results demonstrate that the viral VEGF, while recognizing a unique profile of the known VEGF receptors (receptor 2 and neuropilin 1), is able to stimulate a striking proliferation of blood vessels in the dermis underlying the site of infection. Furthermore, the data demonstrate that the viral VEGF participates in promoting a distinctive pattern of epidermal proliferation. Loss of a functional viral VEGF resulted in lesions with markedly reduced clinical indications of infection. However, viral replication in the early stages of infection was not impaired, and only at later times did it appear that replication of the recombinant virus might be reduced.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-like protein from orf virus NZ2 binds to VEGFR2 and neuropilin-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 16;96(6):3071-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.3071. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10077638 Free PMC article.
-
Major amino acid sequence variants of viral vascular endothelial growth factor are functionally equivalent during Orf virus infection of sheep skin.Virus Res. 2007 Sep;128(1-2):115-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.04.018. Epub 2007 May 23. Virus Res. 2007. PMID: 17524510
-
Vascular endothelial growth factors encoded by Orf virus show surprising sequence variation but have a conserved, functionally relevant structure.J Gen Virol. 2002 Nov;83(Pt 11):2845-2855. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-11-2845. J Gen Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388821
-
Immunity and counter-immunity during infection with the parapoxvirus orf virus.Virus Res. 2002 Sep;88(1-2):3-16. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00117-x. Virus Res. 2002. PMID: 12297324 Review.
-
Ovine diseases. Orf.Vet Res. 1998 May-Aug;29(3-4):311-26. Vet Res. 1998. PMID: 9689744 Review.
Cited by
-
Ankyrin Repeat Proteins of Orf Virus Influence the Cellular Hypoxia Response Pathway.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01430-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01430-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795413 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomics of the midgut microbiome of Rhipicephalus microplus from China.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Feb 8;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05161-6. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35135613 Free PMC article.
-
ORFV: a novel oncolytic and immune stimulating parapoxvirus therapeutic.Mol Ther. 2012 Jun;20(6):1148-57. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.301. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Mol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22273579 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine-Binding Proteins Encoded by Parapoxvirus of Red Deer of New Zealand Display Evidence of Gene Duplication and Divergence of Ligand Specificity.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1421. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01421. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31293551 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion and collapse of VEGF diversity in major clades of the animal kingdom.Angiogenesis. 2023 Aug;26(3):437-461. doi: 10.1007/s10456-023-09874-9. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Angiogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37017884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arkonac B M, Foster L C, Sibinga N E, Patterson C, Lai K, Tsai J C, Lee M E, Perrella M A, Haber E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4400–4405. - PubMed
-
- Bielenberg D R, Bucana C D, Sanchez R, Donawho C K, Kripke M L, Fidler I J. Molecular regulation of UVB-induced cutaneous angiogenesis. J Investig Dermatol. 1998;111:864–872. - PubMed
-
- Bielenberg D R, Bucana C D, Sanchez R, Mulliken J B, Folkman J, Fidler I J. Progressive growth of infantile cutaneous hemangiomas is directly correlated with hyperplasia and angiogenesis of adjacent epidermis and inversely correlated with expression of the endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor, IFN-beta. Int J Oncol. 1999;14:401–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

