Replication of wild-type and mutant human cytomegalovirus in life-extended human diploid fibroblasts
- PMID: 11044129
- PMCID: PMC110959
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10816-10818.2000
Replication of wild-type and mutant human cytomegalovirus in life-extended human diploid fibroblasts
Abstract
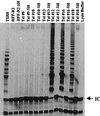
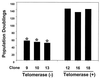
A cDNA encoding the catalytic subunit of human telomerase was used to generate life-extended derivatives of primary human diploid fibroblasts. The life-extended cells supported efficient human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) replication. A subclone of the life-extended cells was generated containing the HCMV UL82 gene and used to isolate and propagate a virus that exhibited a profound growth defect after infection at a low input multiplicity.
Figures

References
-
- Bodnar A G, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt S E, Chiu C P, Morin G B, Harley C B, Shay J W, Lichtsteiner S, Wright W E. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science. 1998;279:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Boeckh M, Gleaves C A, Bindra R, Meyers J D. Comparison of MRC-5 and U-373MG astrocytoma cells for detection of cytomegalovirus in shell vial centrifugation cultures. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;10:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Ho D D, Rota T R, Andrews C A, Hirsch M S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1984;150:956–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

