Identification of a locus for autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease, on chromosome 19p13.2-13.1
- PMID: 11047756
- PMCID: PMC1287938
- DOI: 10.1086/316904
Identification of a locus for autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease, on chromosome 19p13.2-13.1
Abstract
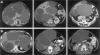
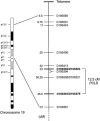
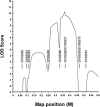
Polycystic liver disease (PCLD) is characterized by the growth of fluid-filled cysts of biliary epithelial origin in the liver. Although the disease is often asymptomatic, it can, when severe, lead to complications requiring surgical therapy. PCLD is most often associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD); however, families with an isolated polycystic liver phenotype without kidney involvement have been described. The clinical presentation and histological features of polycystic liver disease in the presence or absence of ADPKD are indistinguishable, raising the possibility that the pathogenetic mechanisms in the diseases are interrelated. We ascertained two large families with polycystic liver disease without kidney cysts and performed a genomewide scan for genetic linkage. A causative gene, PCLD, was mapped to chromosome 19p13.2-13.1, with a maximum LOD score of 10.3. Haplotype analysis refined the PCLD interval to 12.5 cM flanked by D19S586/D19S583 and D19S593/D19S579. The discovery of genetic linkage will facilitate diagnosis and study of this underdiagnosed disease entity. Identification of PCLD will be instrumental to an understanding of the pathogenesis of cyst formation in the liver in isolated PCLD and in ADPKD.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Chromosome 19–p Arm Metric Physical Map, http://greengenes.llnl.gov/genome-bin/loadmap?region=mp
-
- Genome Database, The, http://www.gdb.org (for Marshfield sex-averaged linkage map)
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/sets/Combo8Frames.htm
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for ADPKD [MIM 173900 and MIM 173910] and PCLD [MIM 174050])
References
-
- Bear JC, Parfrey PS, Morgan JM, Martin CJ, Cramer BC (1992) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: new information for genetic counseling. Am J Med Genet 43:548–553 - PubMed
-
- Cai Y, Maeda Y, Cedzich A, Torres VE, Wu G, Hayashi T, Mochizuki T, Park JH, Witzgall R, Somlo S (1999) Identification and characterization of polycystin-2, the PKD2 gene product. J Biol Chem 274:28557–28565 - PubMed
-
- Caremani M, Vincenti A, Benci A, Sassoli S, Tacconi D (1993) Ecographic epidemiology of non-parasitic hepatic cysts. J Clin Ultrasound 21:115–118 - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry AZ, Lyons GE, Gronostajski RM (1997) Expression patterns of the four nuclear factor I genes during mouse embryogenesis indicate a potential role in development. Dev Dyn 208:313–325 - PubMed
-
- Comfort MW, Gray HK, Dahlin DC, Whitesell FB (1952) Polycystic disease of the liver: a study of 24 cases. Gastroenterology 20:60–78 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

