Long-term potentiation induced by theta frequency stimulation is regulated by a protein phosphatase-1-operated gate
- PMID: 11050107
- PMCID: PMC6772713
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-21-07880.2000
Long-term potentiation induced by theta frequency stimulation is regulated by a protein phosphatase-1-operated gate
Abstract
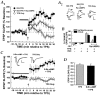
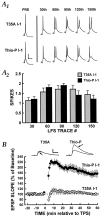
Long-term potentiation (LTP) can be induced in the Schaffer collateral-->CA1 synapse of hippocampus by stimulation in the theta frequency range (5-12 Hz), an effect that depends on activation of the cAMP pathway. We investigated the mechanisms of the cAMP contribution to this form of LTP in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. theta pulse stimulation (TPS; 150 stimuli at 10 Hz) by itself did not induce LTP, but the addition of either the beta-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol or the cAMP analog 8-bromo-cAMP (8-Br-cAMP) enabled TPS-induced LTP. The isoproterenol effect was blocked by postsynaptic inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Several lines of evidence indicated that cAMP enabled LTP by blocking postsynaptic protein phosphatase-1 (PP1). Activators of the cAMP pathway reduced PP1 activity in the CA1 region and increased the active form of inhibitor-1, an endogenous inhibitor of PP1. Postsynaptic injection of activated inhibitor-1 mimicked the LTP-enabling effect of cAMP pathway stimulation. TPS evoked complex spiking when isoproterenol was present. However, complex spiking was not sufficient to enable TPS-induced LTP, which additionally required the inhibition of postsynaptic PP1. PP1 inhibition seems to promote the activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMKII), because (1) a CaMKII inhibitor blocked the induction of LTP by TPS paired with either isoproterenol or activated inhibitor-1 and (2) CaMKII in area CA1 was activated by the combination of TPS and 8-Br-cAMP but not by either stimulus alone. These results indicate that the cAMP pathway enables TPS-induced LTP by inhibiting PP1, thereby enhancing Ca(2+)-independent CaMKII activity.
Figures



References
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Wong T, Nouranifar R, Iyengar R, Landau EM. Postsynaptic cAMP pathway gates early LTP in hippocampal CA1 region. Neuron. 1995;15:1403–1414. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Connor JH, Brown GP, Wong T, Shenolikar S, Iyengar R, Landau EM. Gating of CaMKII by cAMP-regulated protein phosphatase activity during LTP. Science. 1998;280:1940–1942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
