Condensed complexes, rafts, and the chemical activity of cholesterol in membranes
- PMID: 11050164
- PMCID: PMC18778
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.220418097
Condensed complexes, rafts, and the chemical activity of cholesterol in membranes
Abstract
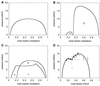
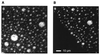
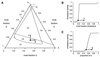
Epifluorescence microscopy studies of mixtures of phospholipids and cholesterol at the air-water interface often exhibit coexisting liquid phases. The properties of these liquids point to the formation of "condensed complexes" between cholesterol and certain phospholipids, such as sphingomyelin. It is found that monolayers that form complexes can incorporate a low concentration of a ganglioside G(M1). This glycolipid is visualized by using a fluorescently labeled B subunit of cholera toxin. Three coexisting liquid phases are found by using this probe together with a fluorescent phospholipid probe. The three liquid phases are identified as a phospholipid-rich phase, a cholesterol-rich phase, and a condensed complex-rich phase. The cholera toxin B labeled ganglioside G(M1) is found exclusively in the condensed complex-rich phase. Condensed complexes are likely present in animal cell membranes, where they should facilitate the formation of specialized domains such as rafts. Condensed complexes also have a major effect in determining the chemical activity of cholesterol. It is suggested that this chemical activity plays an essential role in the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis. Gradients in the chemical activity of cholesterol should likewise govern the rates and direction of intracellular intermembrane cholesterol transport.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid rafts reconstituted in model membranes.Biophys J. 2001 Mar;80(3):1417-28. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76114-0. Biophys J. 2001. PMID: 11222302 Free PMC article.
-
Condensed complexes of cholesterol and phospholipids.Biophys J. 1999 Sep;77(3):1507-17. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76998-5. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10465761 Free PMC article.
-
Critical points in charged membranes containing cholesterol.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 15;99(21):13391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.212522699. Epub 2002 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12368466 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid immiscibility in membranes.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:469-92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141704. Epub 2003 Jan 31. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12574063 Review.
-
Condensed complexes of cholesterol and phospholipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Mar 10;1610(2):159-73. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(03)00015-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12648771 Review.
Cited by
-
Palmitoylated Proteins in Dendritic Spine Remodeling.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020 Jun 16;12:22. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00022. eCollection 2020. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32655390 Free PMC article.
-
Use of cyclodextrin for AFM monitoring of model raft formation.Biophys J. 2004 Feb;86(2):861-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(04)74161-2. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 14747321 Free PMC article.
-
Assess the nature of cholesterol-lipid interactions through the chemical potential of cholesterol in phosphatidylcholine bilayers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 27;104(13):5372-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611450104. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17372226 Free PMC article.
-
The Chemical Potential of Plasma Membrane Cholesterol: Implications for Cell Biology.Biophys J. 2018 Feb 27;114(4):904-918. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.12.042. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29490250 Free PMC article.
-
Complexation of phosphatidylcholine lipids with cholesterol.Biophys J. 2004 Mar;86(3):1345-56. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74206-X. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 14990465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feingold L. Cholesterol in Membrane Models. Ann Arbor, MI: CRC; 1993.
-
- Leathes J B. Lancet. 1925;208:853–856.
-
- Albrecht O, Gruler H, Sackmann E. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1981;79:319–338.
-
- Chapman D. In: Membrane Models and the Formation of Biological Membranes. Bolis L, Pethica B A, editors. New York: Interscience; 1968. pp. 6–19.
-
- Phillips M C. Prog Surf Membr Sci. 1972;5:139–221.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

