Synthesis and characterization of selenotrisulfide-derivatives of lipoic acid and lipoamide
- PMID: 11050172
- PMCID: PMC18789
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.220426897
Synthesis and characterization of selenotrisulfide-derivatives of lipoic acid and lipoamide
Abstract
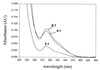
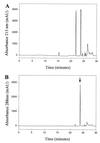
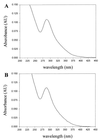
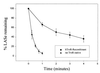
Thiol-containing compounds, such as glutathione and cysteine, react with selenite under specific conditions to form selenotrisulfides. Previous studies have focused on isolation and characterization of intermolecular selenotrisulfides. This study describes the preparation and characterization of intramolecular selenotrisulfide derivatives of lipoic acid and lipoamide. These derivatives, after separation from other reaction products by reverse-phase HPLC, exhibit an absorbance maximum at 288 nm with an extinction coefficient of 1,500 M(-1) small middle dotcm(-1). The selenotrisulfide derivative of lipoic acid was significantly stable at or below pH 8.0 in contrast to several other previously studied selenotrisulfides. Mass spectral analysis of the lipoic acid and lipoamide derivatives confirmed both the expected molecular weights and also the presence of a single atom of selenium as revealed by its isotopic distribution. The selenotrisulfide derivative of lipoic acid was found to serve as an effective substrate for recombinant human thioredoxin reductase as well as native rat thioredoxin reductase in the presence of NADPH. Likewise, the lipoamide derivative was efficiently reduced by NADH-dependent bovine lipoamide dehydrogenase. The significant in vitro stability of these intramolecular selenotrisulfide derivatives of lipoic acid can serve as an important asset in the study of such selenium adducts as model selenium donor compounds for selenophosphate biosynthesis and as rate enhancement effectors in various redox reactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficient reduction of lipoamide and lipoic acid by mammalian thioredoxin reductase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996 Aug 5;225(1):268-74. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.1165. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996. PMID: 8769129
-
Glutathione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase have opposite stereospecificities for alpha-lipoic acid enantiomers.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 17;206(2):724-30. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1102. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. PMID: 7826393
-
Assay of protein-bound lipoic acid in tissues by a new enzymatic method.Anal Biochem. 1998 May 1;258(2):299-304. doi: 10.1006/abio.1998.2615. Anal Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9570844
-
Regeneration of the antioxidant ubiquinol by lipoamide dehydrogenase, thioredoxin reductase and glutathione reductase.Biofactors. 2003;18(1-4):45-50. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520180206. Biofactors. 2003. PMID: 14695919 Review.
-
[Alpha-lipoic--dihydrolipoic acids--active bioantioxidant and bioregulatory system].Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2005 May-Jun;77(3):20-6. Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2005. PMID: 16566124 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of selenium metabolism in the oral pathogen Treponema denticola.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(12):4035-40. doi: 10.1128/JB.00164-09. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19363113 Free PMC article.
-
Two birds with one stone: doing metabolomics with your proteomics kit.Proteomics. 2013 Dec;13(23-24):3371-86. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201300192. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 24155035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemoglobin-mediated selenium export from red blood cells.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008 Mar;13(3):471-9. doi: 10.1007/s00775-007-0335-6. Epub 2008 Jan 4. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2008. PMID: 18175156
-
Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A participates in the selenium transport into the rat brain.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021 Dec;26(8):933-945. doi: 10.1007/s00775-021-01903-6. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34550449
-
High affinity selenium uptake in a keratinocyte model.FEBS Lett. 2008 Jan 23;582(2):299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.12.022. Epub 2007 Dec 26. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 18154736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Painter H E. Chem Rev. 1941;28:179–213.
-
- Ganther H E. Biochemistry. 1968;7:2898–2905. - PubMed
-
- Kice J L, Lee T W S, Pan S. J Amer Chem Soc. 1980;102:4448–4455.
-
- Nakagawa T, Aoyama E, Kobayashi N, Tanaka H, Chikuma M, Sakurai H, Nakayama M. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;150:1149–1154. - PubMed
-
- Ganther H E. Biochemistry. 1971;10:4089–4098. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

