Phosphorylation near nuclear localization signal regulates nuclear import of adenomatous polyposis coli protein
- PMID: 11050185
- PMCID: PMC18806
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.230435597
Phosphorylation near nuclear localization signal regulates nuclear import of adenomatous polyposis coli protein
Abstract
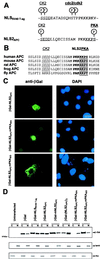
Mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene is an early step in the development of colorectal carcinomas. APC protein is located in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The objective of this study was to define the nuclear localization signals (NLSs) in APC protein. APC contains two potential NLSs comprising amino acids 1767-1772 (NLS1(APC)) and 2048-2053 (NLS2(APC)). Both APC NLSs are well conserved among human, mouse, rat, and fly. NLS1(APC) and NLS2(APC) each were sufficient to target the cytoplasmic protein beta-galactosidase to the nucleus. Mutational analysis of APC demonstrated that both NLSs were necessary for optimal nuclear import of full-length APC protein. Alignment of NLS2(APC) with the simian virus 40 large T antigen NLS (NLS(SV40 T-ag)) revealed sequence similarity extending to adjacent phosphorylation sites. Changing a serine residue (Ser(2054)) to aspartic acid mutated the potential protein kinase A site adjacent to NLS2(APC), resulting in both inhibition of the NLS2(APC)-mediated nuclear import of a chimeric beta-galactosidase fusion protein and a reduction of full-length APC nuclear localization. Our data provide evidence that control of APC's nuclear import through phosphorylation is a potential mechanism for regulating APC's nuclear activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cell density and phosphorylation control the subcellular localization of adenomatous polyposis coli protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Dec;21(23):8143-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.8143-8156.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11689703 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of nuclear import and export signals within Fli-1: roles of the nuclear import signals in Fli-1-dependent activation of megakaryocyte-specific promoters.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3087-108. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3087-3108.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798196 Free PMC article.
-
A protein kinase CK2 site flanking the nuclear targeting signal enhances nuclear transport of human cytomegalovirus ppUL44.Traffic. 2005 Nov;6(11):1002-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00331.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16190981
-
Nuclear APC.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;656:13-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1145-2_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19928349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of protein transport to the nucleus: central role of phosphorylation.Physiol Rev. 1996 Jul;76(3):651-85. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1996.76.3.651. Physiol Rev. 1996. PMID: 8757785 Review.
Cited by
-
An entropy-based gene selection method for cancer classification using microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Mar 24;6:76. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-76. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15790388 Free PMC article.
-
Cell density and phosphorylation control the subcellular localization of adenomatous polyposis coli protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Dec;21(23):8143-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.8143-8156.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11689703 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation by casein kinase 1 regulates tonicity-induced osmotic response element-binding protein/tonicity enhancer-binding protein nucleocytoplasmic trafficking.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 20;283(25):17624-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800281200. Epub 2008 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18411282 Free PMC article.
-
APC-mediated downregulation of beta-catenin activity involves nuclear sequestration and nuclear export.EMBO Rep. 2000 Dec;1(6):519-23. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd117. EMBO Rep. 2000. PMID: 11263497 Free PMC article.
-
Adenomatous polyposis coli protein associates with C/EBP beta and increases Bacillus anthracis edema toxin-stimulated gene expression in macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19364-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.224543. Epub 2011 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21487015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, et al. Cell. 1991;66:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Joslyn G, Carlson M, Thliveris A, Albertsen H, Gelbert L, Samowitz W, Groden J, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, et al. Cell. 1991;66:601–613. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler K, Nilbert M, Vogelstein B, Bryan T, Levy D, Smith K, Presinger A C, Hamilton S R, Hedge P, Markham A, et al. Science. 1991;251:1366–1370. - PubMed
-
- Nishisho I, Nakamura Y, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y, Ando H, Horii A, Koyama K, Utsunomiya J, Baba S, Hedge P, et al. Science. 1991;253:665–668. - PubMed
-
- Powell S M, Zilz N, Beazer-Barclay Y, Bryan T M, Hamilton S R, Thibodeau S N, Vogelstein B, Kinzler K W. Nature (London) 1992;359:235–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

