Anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody treatment in rheumatic disease
- PMID: 11053081
- PMCID: PMC1766618
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i21
Anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody treatment in rheumatic disease
Abstract
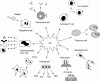
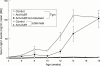
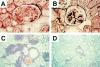
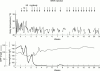
Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a pleiotropic cytokine with a wide range of biological activities. IL6 transgene into mice gives rise to the abnormalities such as hypergammaglobulinaemia, thrombocytosis, infiltration of inflammatory cells into the tissues, mesangial cell proliferation of the kidney as well as splenomegaly and lymphadenopathy, which are predictable by the biological functions of IL6 shown in vitro. Continuous overproduction of IL6 is observed in patients with some immune-inflammatory diseases such as Castleman's disease and rheumatoid arthritis that are frequently associated with similar abnormalities to those of IL6 transgenic mice, strongly suggesting the involvement of IL6 in the human diseases. Successful treatment of the model animals for immune-inflammatory diseases with anti-IL6 receptor (IL6R) antibody thus indicates the possible application of IL6 blocking agents to treat the IL6 related immune-inflammatory diseases of humans. In this review, the new therapeutic strategy for Castleman's disease and RA using humanized antibody to human IL6 receptor, MRA, is discussed.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

