Role of interleukin 1 and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the mediation of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 11053099
- PMCID: PMC1766616
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i103
Role of interleukin 1 and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the mediation of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
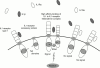
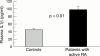
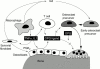
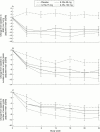
Chronic arthritis is characterised by chronic joint inflammation and concurrent joint erosion and destruction. The inflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 (IL1) has been shown to be a key mediator in the autoimmune disease rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Interleukin 1 mediates bone resorption and cartilage destruction, but may not play as dominant a part in joint swelling and inflammation. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL1Ra) selectively inhibits the effects of IL1 by competing for the IL1 receptor on all surfaces of the synovium. In a randomised controlled trial in 472 patients with active disease, IL1Ra 30 mg/day, 75 mg/day or 150 mg/day given by subcutaneous injection significantly reduced the signs and symptoms of RA at 24 weeks. An American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 20% response was seen in 43% of the patients treated with 150 mg/day at 24 weeks. IL1Ra was well tolerated; injection site reactions were the most common adverse event. In another trial, in 419 patients with active RA treated concomitantly with methotrexate, there were ACR 20% responses after 24 weeks in 42% of the patients treated with 1 mg/kg/day by subcutaneous injection and in 35% of those treated with 2 mg/kg/day. I1Ra offers a unique selective, targeted mechanism of action to block the IL1 mediated effects of RA.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

