Isolation and use of a homologous histone H4 promoter and a ribosomal DNA region in a transformation vector for the oil-producing fungus Mortierella alpina
- PMID: 11055907
- PMCID: PMC92363
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.11.4655-4661.2000
Isolation and use of a homologous histone H4 promoter and a ribosomal DNA region in a transformation vector for the oil-producing fungus Mortierella alpina
Abstract
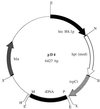
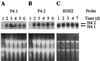
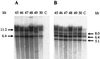
Mortierella alpina was transformed successfully to hygromycin B resistance by using a homologous histone H4 promoter to drive gene expression and a homologous ribosomal DNA region to promote chromosomal integration. This is the first description of transformation in this commercially important oleaginous organism. Two pairs of histone H3 and H4 genes were isolated from this fungus. Each pair consisted of one histone H3 gene and one histone H4 gene, transcribed divergently from an intergenic promoter region. The pairs of encoded histone H3 or H4 proteins were identical in amino acid sequence. At the DNA level, each histone H3 or H4 open reading frame showed 97 to 99% identity to its counterpart but the noncoding regions had little sequence identity. Unlike the histone genes from other filamentous fungi, all four M. alpina genes lacked introns. During normal vegetative growth, transcripts from the two histone H4 genes were produced at approximately the same level, indicating that either histone H4 promoter could be used in transformation vectors. The generation of stable, hygromycin B-resistant transformants required the incorporation of a homologous ribosomal DNA region into the transformation vector to promote chromosomal integration.
Figures
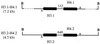



References
-
- Arnau J, Strøman P. Gene replacement and ectopic integration in the zygomycete Mucor circinelloides. Curr Genet. 1993;23:542–546. - PubMed
-
- Benito E P, Díaz-Mínguez J M, Iturriaga E A, Campuzano V, Eslava A P. Cloning and sequence analysis of the Mucor circinelloides pyrG gene encoding orotidine-5′-monophosphate decarboxylase: use of pyrG for homologous transformation. Gene. 1992;116:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Bilgin M, Dedeoglu D, Omirulleh S, Peres A, Engler G, Inzé D, Dudits D, Fehér A. Meristem, cell division and S phase-dependent activity of wheat histone H4 promoter in transgenic maize plants. Plant Sci. 1999;143:35–44.
-
- Burmester A. Analysis of the gene for the elongation factor 1α from the zygomycete Absidia glauca. Use of the promoter region for constructions of transformation vectors. Microbiol Res. 1995;150:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Burmester A, Wöstemeyer A, Wöstemeyer J. Integrative transformation of a zygomycete, Absidia glauca, with vectors containing repetitive DNA. Curr Genet. 1990;17:155–161.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

