Assessment of poliovirus eradication in Japan: genomic analysis of polioviruses isolated from river water and sewage in toyama prefecture
- PMID: 11055968
- PMCID: PMC92424
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.11.5087-5091.2000
Assessment of poliovirus eradication in Japan: genomic analysis of polioviruses isolated from river water and sewage in toyama prefecture
Abstract
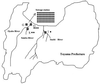
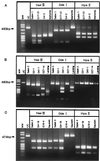
Seventy-eight poliovirus strains isolated from river water and sewage in Toyama Prefecture, Japan, during 1993 to 1995 were characterized by the PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method and by partially sequencing the VP3 and VP1 regions of the viral genome. Of these isolates, 36 were identified as Sabin vaccine strains, and 42 were identified as vaccine variant strains that had less than 1.4% nucleotide divergence from the Sabin strains, including 7 isolates with patterns different from those of Sabin strains as determined by PCR-RFLP analysis. These findings suggest that wild-type poliovirus was not circulating in Toyama Prefecture.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander J P, Jr, Gary H E, Jr, Pallansch M A. Duration of poliovirus excretion and its implications for acute flaccid paralysis surveillance: a review of the literature. J Infect Dis. 1997;175(Suppl. 1):S176–S182. - PubMed
-
- Balanant J, Guillot S, Candrea A, Delpeyroux F, Crainic R. The natural genomic variability of poliovirus analyzed by a restriction fragment length polymorphism assay. Virology. 1991;184:645–654. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress toward global eradication of poliomyelitis, 1996. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:579–584. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress toward global eradication of poliomyelitis, 1997. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47:414–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

